OsmC proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium smegmatis protect against organic hydroperoxide stress
- PMID: 22088319
- PMCID: PMC3249001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tube.2011.10.021
OsmC proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium smegmatis protect against organic hydroperoxide stress
Abstract
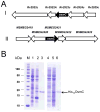
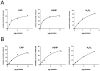
Bacterial antioxidants play a critical role in the detoxification of endogenously and host derived oxidative radicals during host-pathogen interactions. Recently, the osmotically induced bacterial protein C (OsmC) is included in the antioxidant category of enzymes as it shows structural and functional relationships with organic hydroperoxide reductase (Ohr) enzyme. A copy of the gene encoding OsmC is conserved across mycobacterial species, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Rv2923c) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (MSMEG2421), but its role in protecting these species against oxidative stress is unknown. To determine the role of OsmC in mycobacterial oxidative stress, we overexpressed and purified OsmCs of M. tuberculosis and M. smegmatis and assessed their ability to reduce peroxide substrates like hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)), cumene hydroperoxide (CHP) and t-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) in Ferrous Ion Oxidation in Xylenol (FOX) assay. This revealed that OsmCs from both species were capable of reducing both inorganic (H(2)O(2)) and organic (CHP and t-BHP) peroxides. Further, an M. smegmatis mutant (MS∆osmC) deficient in OsmC exhibited reduced reduction of CHP and t-BHP than the parental wild type strain, indicating that OsmC protein contributes significantly for the total peroxide reductase activity of mycobacteria. The MS∆osmC strain was also sensitive to organic hydroperoxides, which could be reversed by complementing with a plasmid borne osmC. Plasmid borne osmC also increased the resistance of M. smegmatis wild type strain to isoniazid (INH) but at a relatively lower level than ahpC, an organic hydroperoxide reductase. These results suggest that OsmC plays an important role in peroxide metabolism and protecting mycobacteria against oxidative stress.
Keywords: INH; Ohr; OsmC; antioxidants; evasion; macrophage; mycobacteria; organic hydroperoxides; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests
Figures
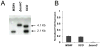
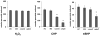
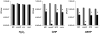
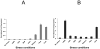
Similar articles
-
Inactivation of the organic hydroperoxide stress resistance regulator OhrR enhances resistance to oxidative stress and isoniazid in Mycobacterium smegmatis.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jan 1;197(1):51-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.02252-14. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25313389 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress response and its role in sensitivity to isoniazid in mycobacteria: characterization and inducibility of ahpC by peroxides in Mycobacterium smegmatis and lack of expression in M. aurum and M. tuberculosis.J Bacteriol. 1996 Jun;178(12):3641-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.12.3641-3649.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8655566 Free PMC article.
-
OsmC in Corynebacterium glutamicum was a thiol-dependent organic hydroperoxide reductase.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Sep 1;136:642-652. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.047. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31195044
-
AhpC, oxidative stress and drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Biofactors. 1999;10(2-3):211-7. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520100219. Biofactors. 1999. PMID: 10609885 Review.
-
Ohr - OhrR, a neglected and highly efficient antioxidant system: Structure, catalysis, phylogeny, regulation, and physiological roles.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 May 20;185:6-24. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.04.001. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35452809 Review.
Cited by
-
Inactivation of the organic hydroperoxide stress resistance regulator OhrR enhances resistance to oxidative stress and isoniazid in Mycobacterium smegmatis.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jan 1;197(1):51-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.02252-14. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25313389 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Response of Rifampicin with Hydroperoxides on Mycobacterium: A Mechanistic Study.Front Microbiol. 2017 Oct 31;8:2075. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02075. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29163385 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the molecular physiology of lantibiotic NAI-107 production in Microbispora ATCC-PTA-5024.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jan 12;17:42. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2369-z. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26754974 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of stress responsive genes enables Limosilactobacillus reuteri to cross-protection against acid, bile salt, and freeze-drying.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 30;15:1437803. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1437803. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39403086 Free PMC article.
-
The msaABCR Operon Regulates the Response to Oxidative Stress in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2019 Oct 4;201(21):e00417-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00417-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31427392 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

