Constitutive coupling of a naturally occurring human alpha1a-adrenergic receptor genetic variant to EGFR transactivation pathway
- PMID: 22089237
- PMCID: PMC3241756
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1116271108
Constitutive coupling of a naturally occurring human alpha1a-adrenergic receptor genetic variant to EGFR transactivation pathway
Abstract
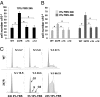
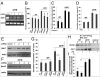
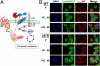
We previously identified a naturally occurring human SNP, G247R, in the third intracellular loop of the α(1a)-adrenergic receptor (α(1a)-247R) and demonstrated that constitutive expression of α(1a)-247R results in twofold increased cell proliferation compared with WT. In the present study we elucidate molecular mechanisms and signal transduction pathways responsible for increased cell proliferation unique to α(1a)-247R, but not α(1a)-WT, α(1b), or α(1d)AR subtypes. We show that elevated levels of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase-12 (ADAM12) in α(1a)-247R-expressing cells are responsible for EGF receptor (EGFR) transactivation, downstream ERK activation, and increased cell proliferation; this pathway is confirmed using MMP, EGFR, and ERK inhibitors. We demonstrate that EGFR transactivation and downstream ERK activation depends on increased shedding of heparin-binding EGF. Finally, we demonstrate that knockdown of MMP7 or β-arrestin1 by shRNAs results in attenuation of proliferation of cells expressing α(1a)-247R. Importantly, accelerated cell proliferation triggered by the α(1a)-247R is serum- and agonist-independent, providing unique evidence for constitutive active coupling to the β-arrestin1/MMP/EGFR transactivation pathway by any G protein-coupled receptor. These findings raise the possibility of a previously unexplored mechanism for sympathetically mediated human hypertension triggered by a naturally occurring human genetic variant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alpha1a-Adrenoceptor Genetic Variant Triggers Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Hyperproliferation and Agonist Induced Hypertrophy via EGFR Transactivation Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 16;10(11):e0142787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142787. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26571308 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha1a-adrenoceptor genetic variant induces cardiomyoblast-to-fibroblast-like cell transition via distinct signaling pathways.Cell Signal. 2014 Sep;26(9):1985-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 15. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24835978 Free PMC article.
-
Independent beta-arrestin2 and Gq/protein kinase Czeta pathways for ERK stimulated by angiotensin type 1A receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells converge on transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 1;284(18):11953-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808176200. Epub 2009 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19254952 Free PMC article.
-
The α1-adrenergic receptors: diversity of signaling networks and regulation.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010 Dec;30(6):410-9. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2010.518152. Epub 2010 Oct 18. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010. PMID: 20954794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAMs as mediators of EGF receptor transactivation by G protein-coupled receptors.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Jul;291(1):C1-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00620.2005. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16769815 Review.
Cited by
-
Transducin (β)-like 1 X-linked receptor 1 promotes gastric cancer progression via the ERK1/2 pathway.Oncogene. 2017 Mar 30;36(13):1873-1886. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.352. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27694893 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for altered brain reactivity to norepinephrine in Veterans with a history of traumatic stress.Neurobiol Stress. 2018 Mar 15;8:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2018.03.001. eCollection 2018 Feb. Neurobiol Stress. 2018. PMID: 29888305 Free PMC article.
-
Squamosamide derivative FLZ protects retinal pigment epithelium cells from oxidative stress through activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-AKT signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Oct 17;15(10):18762-75. doi: 10.3390/ijms151018762. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25329617 Free PMC article.
-
Icariside II activates EGFR-Akt-Nrf2 signaling and protects osteoblasts from dexamethasone.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2594-2603. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13732. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27911877 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid response to the alpha-1 adrenergic agent phenylephrine in the perioperative period is impacted by genomics and ancestry.Pharmacogenomics J. 2021 Apr;21(2):174-189. doi: 10.1038/s41397-020-00194-5. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Pharmacogenomics J. 2021. PMID: 33168928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudner XL, et al. Subtype specific regulation of human vascular α(1)-adrenergic receptors by vessel bed and age. Circulation. 1999;100:2336–2343. - PubMed
-
- Autelitano DJ, Woodcock EA. Selective activation of alpha1A-adrenergic receptors in neonatal cardiac myocytes is sufficient to cause hypertrophy and differential regulation of alpha1-adrenergic receptor subtype mRNAs. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998;30:1515–1523. - PubMed
-
- Zusman RM. The role of alpha 1-blockers in combination therapy for hypertension. Int J Clin Pract. 2000;54:36–40. - PubMed
-
- Rockman HA, Koch WJ, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane-spanning receptors and heart function. Nature. 2002;415:206–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

