Cell type-specific three-dimensional structure of thalamocortical circuits in a column of rat vibrissal cortex
- PMID: 22089425
- PMCID: PMC3432239
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhr317
Cell type-specific three-dimensional structure of thalamocortical circuits in a column of rat vibrissal cortex
Abstract
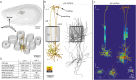
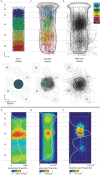
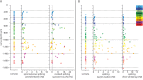
Soma location, dendrite morphology, and synaptic innervation may represent key determinants of functional responses of individual neurons, such as sensory-evoked spiking. Here, we reconstruct the 3D circuits formed by thalamocortical afferents from the lemniscal pathway and excitatory neurons of an anatomically defined cortical column in rat vibrissal cortex. We objectively classify 9 cortical cell types and estimate the number and distribution of their somata, dendrites, and thalamocortical synapses. Somata and dendrites of most cell types intermingle, while thalamocortical connectivity depends strongly upon the cell type and the 3D soma location of the postsynaptic neuron. Correlating dendrite morphology and thalamocortical connectivity to functional responses revealed that the lemniscal afferents can account for some of the cell type- and location-specific subthreshold and spiking responses after passive whisker touch (e.g., in layer 4, but not for other cell types, e.g., in layer 5). Our data provides a quantitative 3D prediction of the cell type-specific lemniscal synaptic wiring diagram and elucidates structure-function relationships of this physiologically relevant pathway at single-cell resolution.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Simulation of signal flow in 3D reconstructions of an anatomically realistic neural network in rat vibrissal cortex.Neural Netw. 2011 Nov;24(9):998-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2011.06.013. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Neural Netw. 2011. PMID: 21775101
-
The excitatory neuronal network of the C2 barrel column in mouse primary somatosensory cortex.Neuron. 2009 Jan 29;61(2):301-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.12.020. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19186171
-
Cortex is driven by weak but synchronously active thalamocortical synapses.Science. 2006 Jun 16;312(5780):1622-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1124593. Science. 2006. PMID: 16778049
-
Barrel cortex and whisker-mediated behaviors.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Aug;17(4):408-16. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.07.008. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17702566 Review.
-
Mapping functional connectivity in barrel-related columns reveals layer- and cell type-specific microcircuits.Brain Struct Funct. 2007 Sep;212(2):107-19. doi: 10.1007/s00429-007-0147-z. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Brain Struct Funct. 2007. PMID: 17717691 Review.
Cited by
-
The C. elegans Connectome Consists of Homogenous Circuits with Defined Functional Roles.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Sep 8;12(9):e1005021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005021. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27606684 Free PMC article.
-
Pinpointing Morphology and Projection of Excitatory Neurons in Mouse Visual Cortex.Front Neurosci. 2019 Aug 29;13:912. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00912. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31555081 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically Defined Subtypes of Somatostatin-Containing Cortical Interneurons.eNeuro. 2023 Aug 9;10(8):ENEURO.0204-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0204-23.2023. Print 2023 Aug. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37463742 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal cell types and connectivity: lessons from the retina.Neuron. 2014 Sep 17;83(6):1262-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.08.054. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 25233310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic variation of transcriptomic cell types in mouse motor cortex.Nature. 2021 Oct;598(7879):144-150. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2907-3. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33184512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ankerst M, Breunig M, Kriegel HP, Sander J. In: Delis A, Faloutsous C, Ghandeharizadeh S, editors. ACM SIGMOD’99 International Conference on Management of Data; Philadelphia. 1999. OPTICS: ordering points to identify the clustering structure. (PA): ACM Press. p. 49–60.

