Cancer and altered metabolism: potential importance of hypoxia-inducible factor and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases
- PMID: 22089927
- PMCID: PMC4197849
- DOI: 10.1101/sqb.2011.76.010975
Cancer and altered metabolism: potential importance of hypoxia-inducible factor and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases
Abstract
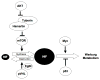
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) deregulation contributes to the Warburg effect. HIF consists of an unstable α subunit and a stable β subunit. In the presence of oxygen, HIFα becomes prolyl hydroxylated by members of the EglN (also called PHD) family, leading to its proteasomal degradation. Under hypoxic conditions, EglN activity is diminished and HIF levels rise. EglN1 is the primary HIF prolyl hydroxylase with EglN2 and EglN3 playing compensatory roles under certain conditions. EglN2 and EglN3 also appear to play HIF-independent roles in regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively. The EglNs belong to a large family of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases that includes the TET DNA hydroxymethylases and JmjC-containing histone demethylases. Members of this superfamily can be inhibited by endogenous metabolites, including fumarate and succinate, which accumulate in tumors that have fumarate hydratase (FH) or succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) mutations, respectively, as well as by the 2-hydroxyglutarate detected in isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutant tumors. 2-Oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases therefore provide a link between altered metabolism and cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Appelhoff RJ, Tian YM, Raval RR, Turley H, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Gleadle JM. Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:38458–38465. - PubMed
-
- Arsham AM, Howell JJ, Simon MC. A novel hypoxia-inducible factor-independent hypoxic response regulating mammalian target of rapamycin and its targets. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:29655–29660. - PubMed
-
- Barrett A, Madsen B, Copier J, Lu PJ, Cooper L, Scibetta AG, Burchell J, Taylor-Papadimitriou J. PLU-1 nuclear protein, which is upregulated in breast cancer, shows restricted expression in normal human adult tissues: a new cancer/testis antigen? Int J Cancer. 2002;101:581–588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
