RNA-related nuclear functions of human Pat1b, the P-body mRNA decay factor
- PMID: 22090346
- PMCID: PMC3248899
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0415
RNA-related nuclear functions of human Pat1b, the P-body mRNA decay factor
Abstract
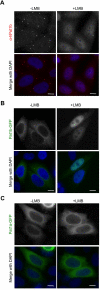
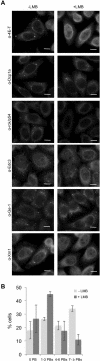
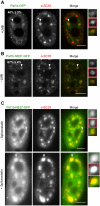
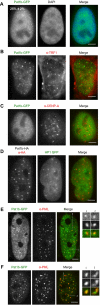
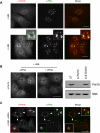
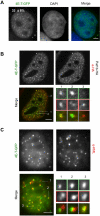
The evolutionarily conserved Pat1 proteins are P-body components recently shown to play important roles in cytoplasmic gene expression control. Using human cell lines, we demonstrate that human Pat1b is a shuttling protein whose nuclear export is mediated via a consensus NES sequence and Crm1, as evidenced by leptomycin B (LMB) treatment. However, not all P-body components are nucleocytoplasmic proteins; rck/p54, Dcp1a, Edc3, Ge-1, and Xrn1 are insensitive to LMB and remain cytoplasmic in its presence. Nuclear Pat1b localizes to PML-associated foci and SC35-containing splicing speckles in a transcription-dependent manner, whereas in the absence of RNA synthesis, Pat1b redistributes to crescent-shaped nucleolar caps. Furthermore, inhibition of splicing by spliceostatin A leads to the reorganization of SC35 speckles, which is closely mirrored by Pat1b, indicating that it may also be involved in splicing processes. Of interest, Pat1b retention in these three nuclear compartments is mediated via distinct regions of the protein. Examination of the nuclear distribution of 4E-T(ransporter), an additional P-body nucleocytoplasmic protein, revealed that 4E-T colocalizes with Pat1b in PML-associated foci but not in nucleolar caps. Taken together, our findings strongly suggest that Pat1b participates in several RNA-related nuclear processes in addition to its multiple regulatory roles in the cytoplasm.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of Rck-Pat1b binding in assembly of processing-bodies.RNA Biol. 2013 Apr;10(4):528-39. doi: 10.4161/rna.24086. Epub 2013 Mar 27. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23535175 Free PMC article.
-
Human Pat1b connects deadenylation with mRNA decapping and controls the assembly of processing bodies.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;30(17):4308-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00429-10. Epub 2010 Jun 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20584987 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins with nuclear export activity: cell cycle-regulated transcription factor ace2p shows cell cycle-independent nucleocytoplasmic shuttling.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(21):8047-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.21.8047-8058.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11027275 Free PMC article.
-
Pat1 RNA-binding proteins: Multitasking shuttling proteins.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Nov;10(6):e1557. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1557. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 31231973 Review.
-
Nucleocytoplasmic transport enters the atomic age.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;13(3):310-9. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00213-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11343901 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA topoisomerase 2-associated proteins PATL1 and PATL2 regulate the biogenesis of hERG K+ channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jan 10;120(2):e2206146120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2206146120. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36608291 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxin-2-like is a regulator of stress granules and processing bodies.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050134. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209657 Free PMC article.
-
Reorganization of Cell Compartmentalization Induced by Stress.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 8;12(10):1441. doi: 10.3390/biom12101441. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of fission yeast Pdc2 in RNA degradation and P-body function.RNA. 2017 Apr;23(4):493-503. doi: 10.1261/rna.059766.116. Epub 2016 Dec 28. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28031482 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the consequences of eIF4E2 (4EHP) interaction with 4E-transporter on its cellular distribution in HeLa cells.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 21;8(8):e72761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072761. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharyya SN, Habermacher R, Martine U, Closs EI, Filipowicz W. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell. 2006;125:1111–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

