High resolution colonoscopy in a bowel cancer screening program improves polyp detection
- PMID: 22090787
- PMCID: PMC3214706
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i38.4308
High resolution colonoscopy in a bowel cancer screening program improves polyp detection
Abstract
Aim: To compare high resolution colonoscopy (Olympus Lucera) with a megapixel high resolution system (Pentax HiLine) as an in-service evaluation.
Methods: Polyp detection rates and measures of performance were collected for 269 colonoscopy procedures. Five colonoscopists conducted the study over a three month period, as part of the United Kingdom bowel cancer screening program.
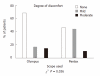
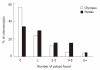
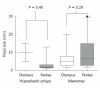
Results: There were no differences in procedure duration (χ² P = 0.98), caecal intubation rates (χ² P = 0.67), or depth of sedation (χ² P = 0.64). Mild discomfort was more common in the Pentax group (χ² P = 0.036). Adenoma detection rate was significantly higher in the Pentax group (χ² test for trend P = 0.01). Most of the extra polyps detected were flat or sessile adenomas.
Conclusion: Megapixel definition colonoscopes improve adenoma detection without compromising other measures of endoscope performance. Increased polyp detection rates may improve future outcomes in bowel cancer screening programs.
Keywords: Bowel cancer screening; High resolution colonoscopy; Polyp detection.
Figures
References
-
- Common cancers - UK mortality statistics. Cancer Research UK. 2010 Available from: http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/cancerstats/mortality/cancerdeaths/
-
- Schrock TR. Colonoscopy versus barium enema in the diagnosis of colorectal cancers and polyps. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1993;3:585–610.
-
- Rex DK, Cutler CS, Lemmel GT, Rahmani EY, Clark DW, Helper DJ, LehmanGA , Mark DG. Colonoscopic miss rates of adenomas determined by back-to-back colonoscopies. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:24–28. - PubMed
-
- Bressler B, Paszat LF, Chen Z, Rothwell DM, Vinden C, Rabeneck L. Rates of new or missed colorectal cancers after colonoscopy and their risk factors: a population-based analysis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:96–102. - PubMed
-
- Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, Polkowski M, Wojciechowska U, Didkowska J, Zwierko M, Rupinski M, Nowacki MP, Butruk E. Quality indicators for colonoscopy and the risk of interval cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1795–1803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

