2,13-Dibenzyl-5,16-diethyl-2,6,13,17-tetra-aza-tricyclo-[16.4.0.0]docosan-2-ium nitrate
- PMID: 22091185
- PMCID: PMC3213608
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811029692
2,13-Dibenzyl-5,16-diethyl-2,6,13,17-tetra-aza-tricyclo-[16.4.0.0]docosan-2-ium nitrate
Abstract
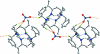
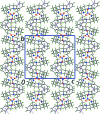
One of the tertiary amine atoms has been protonated in the title salt, C(36)H(57)N(4) (+)·NO(3) (-). The four N atoms of the macrocycle are almost coplanar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0053 Å), a result correlated with the formation of intra-molecular N-H⋯N and N-H⋯(N,N) hydrogen bonds. With respect to this plane, the benzyl groups lie to either side; a similar arrangement pertains for the cyclo-hexyl rings (each with a chair conformation). Helical supra-molecular chains are evident in the crystal, whereby alternating cations and anions are linked by C-H⋯O inter-actions. The chains are consolidated into supra-molecular arrays in the ab plane via C-H⋯π contacts involving both benzene rings.
Figures

References
-
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Choi, J.-H., Clegg, W. & Harrington, R. W. (2010a). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 40, 80–84.
-
- Choi, J.-H., Clegg, W., Harrington, R. W., Yoon, H.-M. & Hong, Y. P. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o644–o646.
-
- Choi, J.-H., Clegg, W. & Nichol, G. S. (2010b). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 636, 1612–1616.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
