Hypoadiponectinemia in obese subjects with type II diabetes: A close association with central obesity indices
- PMID: 22091299
- PMCID: PMC3214388
Hypoadiponectinemia in obese subjects with type II diabetes: A close association with central obesity indices
Abstract
Background: Adiponectin is an adipocyte secreted protein with important biological functions Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and type II diabetes This study aimed to evaluate serum adiponectin level in obese subjects with type II diabetes and its correlation with metabolic parameters
Methods: This cross-sectional study was performed on 40 obese subjects with type II diabetes and 40 non-diabetic obese control subjects Fasting lipid profile was measured by the enzymatic methods The NycoCard HbA1c protocol was used to measure HbAlc The Serum adiponectin, insulin and glucose levels were measured using an enzyme immunoassay and glucose oxidase methods respectively
Results: Type II diabetes was associated with hypoadiponectinemia, in both men and women Serum adiponectin level in non-diabetic subjects (6.44 ± 2.47 μg/ml) was significantly higher than diabetics (4.55 ± 1.88 μg/ml) Furthermore, serum adiponectin concentration in females was significantly higher than males in non-diabetics (7.18 ± 2.68 vs 5.61 ± 0.57) and diabetic groups (5.18 ± 2.08 vs 3.99 ± 1.5) There was a negative and significant correlation between serum adiponectin level with waist (r = -0.451, p = 0.003), waist to hip ratio (r = -0.404, p = 0.01) and BMI (r = - 0.322, p = 0.042) and a positive correlation with HDL (r = 0.337, p = 0.034) in non-diabetic group In diabetic group, there was only found a negative correlation between adiponectin and waist size (r = -0.317, p = 0.046)
Conclusions: Obesity and type II diabetes are associated with low serum adiponectin concentration.
Keywords: Adiponectin; BMI; Obese; Type II diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

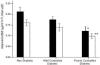
References
-
- Cusi K. The epidemic of type 2 diabetes mellitus: its links to obesity, insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. In: Regensteiner JG, Reusch JE, Stewart KJ, Veves A, editors. Diabetes and Exercise. New York: Springer; 2009. pp. 3–54.
-
- Azizi F. Diabetes care and prevention in Iran. Diabetes Voice. 2005;50(4):15–7.
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(9):1414–31. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(6):2087–102. - PubMed
-
- Cusi K. The role of adipose tissue and lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2010;10(4):306–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
