Signals and regulators that govern Streptomyces development
- PMID: 22092088
- PMCID: PMC3285474
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00317.x
Signals and regulators that govern Streptomyces development
Abstract
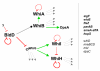
Streptomyces coelicolor is the genetically best characterized species of a populous genus belonging to the gram-positive Actinobacteria. Streptomycetes are filamentous soil organisms, well known for the production of a plethora of biologically active secondary metabolic compounds. The Streptomyces developmental life cycle is uniquely complex and involves coordinated multicellular development with both physiological and morphological differentiation of several cell types, culminating in the production of secondary metabolites and dispersal of mature spores. This review presents a current appreciation of the signaling mechanisms used to orchestrate the decision to undergo morphological differentiation, and the regulators and regulatory networks that direct the intriguing development of multigenomic hyphae first to form specialized aerial hyphae and then to convert them into chains of dormant spores. This current view of S. coelicolor development is destined for rapid evolution as data from '-omics' studies shed light on gene regulatory networks, new genetic screens identify hitherto unknown players, and the resolution of our insights into the underlying cell biological processes steadily improve.
© 2011 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akanuma G, Hara H, Ohnishi Y, Horinouchi S. Dynamic changes in the extracellular proteome caused by absence of a pleiotropic regulator AdpA in Streptomyces griseus. Molecular Microbiology. 2009;73:898–912. - PubMed
-
- Akanuma G, Ueki M, Ishizuka M, Ohnishi Y, Horinouchi S. Control of aerial mycelium formation by the BldK oligopeptide ABC transporter in Streptomyces griseus. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2011;315:54–62. - PubMed
-
- Angell S, Lewis CG, Buttner MJ, Bibb MJ. Glucose repression in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): a likely regulatory role for glucose kinase. Molecular and General Genetics. 1994;244:135–143. - PubMed
-
- Ausmees N, Wahlstedt H, Bagchi S, Elliot MA, Buttner MJ, Flärdh K. SmeA, a small membrane protein with multiple functions in Streptomyces sporulation including targeting of a SpoIIIE/FtsK-like protein to cell division septa. Molecular Microbiology. 2007;65:1458–1473. - PubMed
-
- Aínsa JA, Parry HD, Chater KF. A response regulator-like protein that functions at an intermediate stage of sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) Molecular Microbiology. 1999;34:607–619. - PubMed

