Dysregulated expression of both the costimulatory CD28 and inhibitory CTLA-4 molecules in PB T cells of advanced cervical cancer patients suggests systemic immunosuppression related to disease progression
- PMID: 22094905
- PMCID: PMC3313031
- DOI: 10.1007/s12253-011-9471-y
Dysregulated expression of both the costimulatory CD28 and inhibitory CTLA-4 molecules in PB T cells of advanced cervical cancer patients suggests systemic immunosuppression related to disease progression
Abstract
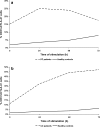
Cervical cancer (CC) occurs more frequently in women who are immunosuppressed, suggesting that both local and systemic immune abnormalities may be involved in the evolution of the disease. Costimulatory CD28 and inhibitory CTLA-4 molecules expressed in T cells play a key role in the balanced immune responses. There has been demonstrated a relation between CD28, CTLA-4, and IFN genes in susceptibility to CC, suggesting their importance in CC development. Therefore, we assessed the pattern of CD28 and CTLA-4 expression in T cells from PB of CC patients with advanced CC (stages III and IV according to FIGO) compared to controls. We also examined the ability of PBMCs to secrete IFN-gamma. We found lower frequencies of freshly isolated and ex vivo stimulated CD4 + CD28+ and CD8 + CD28+ T cells in CC patients than in controls. Loss of CD28 expression was more pronounced in the CD8+ T subset. Markedly increased proportions of CTLA-4+ T cells in CC patients before and after culture compared to controls were also observed. In addition, patients' T cells exhibited abnormal kinetics of surface CTLA-4 expression, with the peak at 24 h of stimulation, which was in contrast to corresponding normal T cells, revealing maximum CTLA-4 expression at 72 h of stimulation. Of note, markedly higher IFN-gamma concentrations were shown in supernatants of stimulated PBMCs from CC patients.
Conclusions: Our report shows the dysregulated CD28 and CTLA-4 expression in PB T cells of CC patients, which may lead to impaired function of these lymphocytes and systemic immunosuppression related to disease progression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The immune checkpoints CTLA-4 and PD-L1 in carcinomas of the uterine cervix.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Jan;216(1):152782. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152782. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 31862202
-
Expression of costimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 and their receptors CD28, CTLA-4 on malignant ascites CD3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from patients with ovarian and other types of peritoneal carcinomatosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Jan;119(1):19-27. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01105.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10606960 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of the expression of T-cell-related costimulatory CD28 and downregulatory CD152 (CTLA-4) molecules in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Br J Cancer. 2004 May 17;90(10):2042-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601833. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15138491 Free PMC article.
-
A transendocytosis perspective on the CD28/CTLA-4 pathway.Adv Immunol. 2014;124:95-136. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800147-9.00004-2. Adv Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25175774 Review.
-
The role of CTLA-4 in the regulation of T cell immune responses.Immunol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;77(1):1-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.1999.00795.x. Immunol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10101680 Review.
Cited by
-
The abscopal effect of immune-radiation therapy in recurrent and metastatic cervical cancer: a narrative review.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 19;14:1201675. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1201675. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37539054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations in components of antiviral or microbial defense as a basis for breast cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2013 Nov;13(4):411-24. doi: 10.1007/s10142-013-0336-1. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Funct Integr Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24057274 Review.
-
Pharmacologic management of advanced cervical cancer: antiangiogenesis therapy and immunotherapeutic considerations.Drugs. 2015 Nov;75(16):1853-65. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0481-z. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26474780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD28-, CD45RA(null/dim) and natural killer-like CD8+ T cells are increased in peripheral blood of women with low-grade cervical lesions.Cancer Cell Int. 2014 Sep 24;14(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12935-014-0097-5. eCollection 2014. Cancer Cell Int. 2014. PMID: 25278812 Free PMC article.
-
The existence of Th22, pure Th17 and Th1 cells in CIN and Cervical Cancer along with their frequency variation in different stages of cervical cancer.BMC Cancer. 2015 Oct 16;15:717. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1767-y. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26474968 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

