Thymic function failure and C-reactive protein levels are independent predictors of all-cause mortality in healthy elderly humans
- PMID: 22095260
- PMCID: PMC3543745
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-011-9341-2
Thymic function failure and C-reactive protein levels are independent predictors of all-cause mortality in healthy elderly humans
Abstract
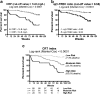
Relationship between thymic function and elderly survival has been suspected, despite the fact that formal proof is elusive due to technical limitations of thymic function-related markers. The newly described sj/β-TREC ratio allows now, by overcoming these limitations, an accurate measurement of thymic output in elderly humans. Thus, the aim of this study was to determine the impact of thymic function and inflammatory markers on healthy elderly human survival. Healthy volunteers (n = 151), aged over 65, were asked to participate (CARRERITAS cohort). Subjects were excluded if diagnosed of dementia or, during the last 6 months, had clinical data of infection, hospital admission, antitumor therapy, or any treatment that could influence the immune status. Thymic function (sj/β-TREC ratio), CD4:CD8 T cell ratio, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and neutrophilia were determined from basal samples. All basal variables and age were associated with 2-year all-cause mortality. Multivariate analysis showed that only thymic function and C-reactive protein were independently associated with time to death. In conclusion, we show, for the first time, the direct role of thymic function in human survival. C-reactive protein raise is also a marker of mortality in the healthy elderly, in a thymic-independent way.
Figures

References
-
- Appay V, Fastenackels S, Katlama C, Ait-Mohand H, Schenider L, Guihot A, Keller M, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Simon A, Lambotte O, Hunt PW, Deeks SG, Costagliola D, Autran B, Sauce D (2011) Old age and anti-CMV immunity are associated with altered T cell reconstitution in HIV-1 infected patients. AIDS. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e32834640e6 - PubMed
-
- Blanco JR, Caro AM, Pérez-Cachafeiro S, Gutiérrez F, Iribarren JA, González-García J, Ferrando-Martínez S, Navarro G, Moreno S. HIV infection and aging. AIDS Rev. 2010;12:218–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
