Effects of whole body vibration on motor unit recruitment and threshold
- PMID: 22096119
- PMCID: PMC3289430
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01223.2010
Effects of whole body vibration on motor unit recruitment and threshold
Abstract
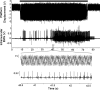
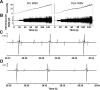
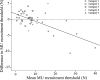
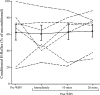
Whole body vibration (WBV) has been suggested to elicit reflex muscle contractions but this has never been verified. We recorded from 32 single motor units (MU) in the vastus lateralis of 7 healthy subjects (34 ± 15.4 yr) during five 1-min bouts of WBV (30 Hz, 3 mm peak to peak), and the vibration waveform was also recorded. Recruitment thresholds were recorded from 38 MUs before and after WBV. The phase angle distribution of all MUs during WBV was nonuniform (P < 0.001) and displayed a prominent peak phase angle of firing. There was a strong linear relationship (r = -0.68, P < 0.001) between the change in recruitment threshold after WBV and average recruitment threshold; the lowest threshold MUs increased recruitment threshold (P = 0.008) while reductions were observed in the higher threshold units (P = 0.031). We investigated one possible cause of changed thresholds. Presynaptic inhibition in the soleus was measured in 8 healthy subjects (29 ± 4.6 yr). A total of 30 H-reflexes (stimulation intensity 30% Mmax) were recorded before and after WBV: 15 conditioned by prior stimulation (60 ms) of the antagonist and 15 unconditioned. There were no significant changes in the relationship between the conditioned and unconditioned responses. The consistent phase angle at which each MU fired during WBV indicates the presence of reflex muscle activity similar to the tonic vibration reflex. The varying response in high- and low-threshold MUs may be due to the different contributions of the mono- and polysynaptic pathways but not presynaptic inhibition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immediate effect of local vibration on motor unit firing behavior and muscle strength in healthy young adult males.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024 Dec;124(12):3707-3717. doi: 10.1007/s00421-024-05553-9. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39110159 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of vibration-induced altered stretch reflex sensitivity on maximal motor unit firing properties.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Jun 1;121(6):2215-2221. doi: 10.1152/jn.00326.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30969899
-
Recruitment of triceps surae motor units in the decerebrate cat. II. Heterogeneity among soleus motor units.J Neurophysiol. 1996 May;75(5):2005-16. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.75.5.2005. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8734599
-
Acute whole-body vibration increases reciprocal inhibition.Hum Mov Sci. 2018 Aug;60:191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Hum Mov Sci. 2018. PMID: 29957423
-
Neuromuscular responses of the plantar flexors to whole-body vibration.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017 Dec;27(12):1569-1575. doi: 10.1111/sms.12803. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017. PMID: 28033657
Cited by
-
Effect of Multi-Frequency Whole-Body Vibration on Muscle Activation, Metabolic Cost and Regional Tissue Oxygenation.IEEE Access. 2020;8:140445-140455. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3011691. Epub 2020 Jul 24. IEEE Access. 2020. PMID: 34036017 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the combination of whole body vibration and shoe with an unstable surface in chronic ankle instability treatment: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2021 Mar 19;13(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13102-021-00256-6. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33741051 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Effect of Whole-Body Vibration on Trunk Endurance and Balance in Obese Female Students: Randomized Controlled Trial.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 14;60(8):1316. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081316. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39202597 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hormonal and neuromuscular responses to mechanical vibration applied to upper extremity muscles.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 4;9(11):e111521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111521. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25368995 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Whole body vibration activates the tonic vibration reflex during voluntary contraction.J Phys Ther Sci. 2023 Jun;35(6):408-413. doi: 10.1589/jpts.35.408. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Phys Ther Sci. 2023. PMID: 37266357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abercromby AFJ, Amonette WE, Layne CS, McFarlin BK, Hinman MR, Paloski WH. Variation in neuromuscular responses during acute whole-body vibration exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39: 1642–1650, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bianconi R, Van Der Meulen JP. The response to vibration of the end organs of mammalian muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol 26: 177–190, 1963 - PubMed
-
- Bressel E, Smith G, Branscomb J. Transmission of whole body vibration in children while standing. Clin Biomech 25: 181–186, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

