Novel mechanisms of central nervous system damage in HIV infection
- PMID: 22096383
- PMCID: PMC3218694
- DOI: 10.2147/hiv.s9186
Novel mechanisms of central nervous system damage in HIV infection
Abstract
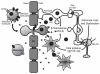
Human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection of the central nervous system is an early event after primary infection, resulting in motor and cognitive defects in a significant number of individuals despite successful antiretroviral therapy. The pathology of the infected brain is characterized by enhanced leukocyte infiltration, microglial activation and nodules, aberrant expression of inflammatory factors, neuronal dysregulation and loss, and blood-brain barrier disruption. Months to years following the primary infection, these central nervous system insults result in a spectrum of motor and cognitive dysfunction, ranging from mild impairment to frank dementia. The mechanisms that mediate impairment are still not fully defined. In this review we discuss the cellular and molecular mechanisms that facilitate impairment and new data that implicate intercellular communication systems, gap junctions and tunneling nanotubes, as mediators of human immunodeficiency virus-1 toxicity and infection within the central nervous system. These data suggest potential targets for novel therapeutics.
Keywords: AIDS; chemokines; dementia; gap junctions; inflammation; nanotubes.
Figures
References
-
- Ellis R, Langford D, Masliah E. HIV and antiretroviral therapy in the brain: neuronal injury and repair. Nature Reviews. 2007;8(1):33–44. - PubMed
-
- Anthony IC, Ramage SN, Carnie FW, Simmonds P, Bell JE. Influence of HAART on HIV-related CNS disease and neuroinflammation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64(6):529–536. - PubMed
-
- McArthur JC, Haughey N, Gartner S, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia: an evolving disease. J Neurovirol. 2003;9(2):205–221. - PubMed
-
- Ances BM, Ellis RJ. Dementia and neurocognitive disorders due to HIV-1 infection. Semin Neurol. 2007;27(1):86–92. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

