Rapid and sensitive hormonal profiling of complex plant samples by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 22098763
- PMCID: PMC3253682
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-4811-7-37
Rapid and sensitive hormonal profiling of complex plant samples by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
Background: Plant hormones play a pivotal role in several physiological processes during a plant's life cycle, from germination to senescence, and the determination of endogenous concentrations of hormones is essential to elucidate the role of a particular hormone in any physiological process. Availability of a sensitive and rapid method to quantify multiple classes of hormones simultaneously will greatly facilitate the investigation of signaling networks in controlling specific developmental pathways and physiological responses. Due to the presence of hormones at very low concentrations in plant tissues (10-9 M to 10-6 M) and their different chemistries, the development of a high-throughput and comprehensive method for the determination of hormones is challenging.
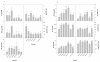
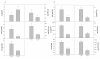
Results: The present work reports a rapid, specific and sensitive method using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization tandem spectrometry (UPLC/ESI-MS/MS) to analyze quantitatively the major hormones found in plant tissues within six minutes, including auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid, 1-amino-cyclopropane-1-carboxyic acid (the ethylene precursor), jasmonic acid and salicylic acid. Sample preparation, extraction procedures and UPLC-MS/MS conditions were optimized for the determination of all plant hormones and are summarized in a schematic extraction diagram for the analysis of small amounts of plant material without time-consuming additional steps such as purification, sample drying or re-suspension.
Conclusions: This new method is applicable to the analysis of dynamic changes in endogenous concentrations of hormones to study plant developmental processes or plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses in complex tissues. An example is shown in which a hormone profiling is obtained from leaves of plants exposed to salt stress in the aromatic plant, Rosmarinus officinalis.
Figures


References
-
- Davies PJ. The plant hormones: their nature, occurrence, and functions. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands; 2010.
-
- Ross JJ, O'Neill DP, Rathbone DA. Auxin-gibberellin interactions in pea: integrating the old with the new. J Plant Growth Regul. 2003;22:99–108. doi: 10.1007/s00344-003-0021-z. - DOI

