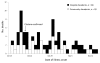Rapid assessment of cholera-related deaths, Artibonite Department, Haiti, 2010
- PMID: 22099119
- PMCID: PMC3310573
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1711.110747
Rapid assessment of cholera-related deaths, Artibonite Department, Haiti, 2010
Abstract
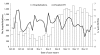
We evaluated a high (6%) cholera case-fatality rate in Haiti. Of 39 community decedents, only 23% consumed oral rehydration salts at home, and 59% did not seek care, whereas 54% of 48 health facility decedents died after overnight admission. Early in the cholera epidemic, care was inadequate or nonexistent.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cholera, 2009. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2010;85:293–308.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: cholera outbreak—Haiti 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010;59:1586–90. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Cholera. Factsheet no 107. Geneva: The Organization; 2010. [cited 2011 Aug 24]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs107/en/index.html
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: cholera outbreak—Haiti, 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010;59:1473–9. - PubMed
-
- Global Task Force on Cholera Control. Cholera outbreak. Assessing the outbreak response and improving preparedness. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004. p. 15 [cited 2011 Aug 24]. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2004/WHO_CDS_CPE_ZFk_2004.4_eng.pdf
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical