Telomere protection by TPP1/POT1 requires tethering to TIN2
- PMID: 22099311
- PMCID: PMC3222871
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.043
Telomere protection by TPP1/POT1 requires tethering to TIN2
Erratum in
-
Telomere Protection by TPP1/POT1 Requires Tethering to TIN2.Mol Cell. 2017 Jul 6;67(1):162. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.033. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28686874 No abstract available.
Abstract
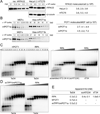
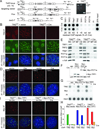
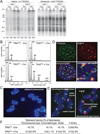
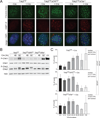
To prevent ATR activation, telomeres deploy the single-stranded DNA binding activity of TPP1/POT1a. POT1a blocks the binding of RPA to telomeres, suggesting that ATR is repressed through RPA exclusion. However, comparison of the DNA binding affinities and abundance of TPP1/POT1a and RPA indicates that TPP1/POT1a by itself is unlikely to exclude RPA. We therefore analyzed the central shelterin protein TIN2, which links TPP1/POT1a (and POT1b) to TRF1 and TRF2 on the double-stranded telomeric DNA. Upon TIN2 deletion, telomeres lost TPP1/POT1a, accumulated RPA, elicited an ATR signal, and showed all other phenotypes of POT1a/b deletion. TIN2 also affected the TRF2-dependent repression of ATM kinase signaling but not to TRF2-mediated inhibition of telomere fusions. Thus, while TIN2 has a minor contribution to the repression of ATM by TRF2, its major role is to stabilize TPP1/POT1a on the ss telomeric DNA, thereby allowing effective exclusion of RPA and repression of ATR signaling.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

