Recessive mutations in ELOVL4 cause ichthyosis, intellectual disability, and spastic quadriplegia
- PMID: 22100072
- PMCID: PMC3234380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.10.011
Recessive mutations in ELOVL4 cause ichthyosis, intellectual disability, and spastic quadriplegia
Abstract
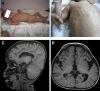
Very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) play important roles in membrane structure and cellular signaling, and their contribution to human health is increasingly recognized. Fatty acid elongases catalyze the first and rate-limiting step in VLCFA synthesis. Heterozygous mutations in ELOVL4, the gene encoding one of the elongases, are known to cause macular degeneration in humans and retinal abnormalities in mice. However, biallelic ELOVL4 mutations have not been observed in humans, and murine models with homozygous mutations die within hours of birth as a result of a defective epidermal water barrier. Here, we report on two human individuals with recessive ELOVL4 mutations revealed by a combination of autozygome analysis and exome sequencing. These individuals exhibit clinical features of ichthyosis, seizures, mental retardation, and spasticity-a constellation that resembles Sjögren-Larsson syndrome (SLS) but presents a more severe neurologic phenotype. Our findings identify recessive mutations in ELOVL4 as the cause of a neuro-ichthyotic disease and emphasize the importance of VLCFA synthesis in brain and cutaneous development.
Copyright © 2011 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Toulmay A., Schneiter R. Lipid-dependent surface transport of the proton pumping ATPase: A model to study plasma membrane biogenesis in yeast. Biochimie. 2007;89:249–254. - PubMed
-
- Leonard A.E., Kelder B., Bobik E.G., Chuang L.T., Lewis C.J., Kopchick J.J., Mukerji P., Huang Y.S. Identification and expression of mammalian long-chain PUFA elongation enzymes. Lipids. 2002;37:733–740. - PubMed
-
- Poulos A., Beckman K., Johnson D.W., Paton B.C., Robinson B.S., Sharp P., Usher S., Singh H. Very long-chain fatty acids in peroxisomal disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1992;318:331–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

