GABAergic transmission in temporal lobe epilepsy: the role of neurosteroids
- PMID: 22101060
- PMCID: PMC3319002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.10.028
GABAergic transmission in temporal lobe epilepsy: the role of neurosteroids
Abstract
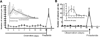
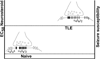
Modification of GABAergic inhibition is an intensely investigated hypothesis guiding research into mechanisms underlying temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). Seizures can be initiated by blocking γ amino butyric acid type A (GABAA receptors, GABARs), which mediate fast synaptic inhibition in the brain, and controlled by drugs that enhance their function. Derivatives of steroid hormones called neurosteroids are natural substances that physiologically enhance GABAR function and suppress seizures. GABAR structure, function, expression, assembly, and pharmacological properties are changed in the hippocampus of epileptic animals. These alterations render GABARs less sensitive to neurosteroid modulation, which may contribute to seizure susceptibility. Plasticity of GABARs could play a role in periodic exacerbation of seizures experienced by women with epilepsy, commonly referred to as catamenial epilepsy.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurosteroid regulation of GABAA receptors: A role in catamenial epilepsy.Brain Res. 2019 Jan 15;1703:31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.031. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 29481795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurosteroid-sensitive δ-GABAA receptors: A role in epileptogenesis?Epilepsia. 2017 Mar;58(3):494-504. doi: 10.1111/epi.13660. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28452419 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic (Genetic) Generalized Epilepsy.2024 Feb 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Feb 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31536218 Free Books & Documents.
-
Receptors with low affinity for neurosteroids and GABA contribute to tonic inhibition of granule cells in epileptic animals.Neurobiol Dis. 2010 Nov;40(2):490-501. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.07.016. Epub 2010 Aug 1. Neurobiol Dis. 2010. PMID: 20682339 Free PMC article.
-
Treatments for seizures in catamenial (menstrual-related) epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 16;9(9):CD013225. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013225.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34528245 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in the neurobiology of epilepsy: a preclinical perspective.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Dec;72 Pt B:180-92. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 25058745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Menstrual Cycle and Oral Contraceptive Phase on Spinal Excitability.PM R. 2016 Sep;8(9):860-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2016.01.013. Epub 2016 Feb 10. PM R. 2016. PMID: 26872589 Free PMC article.
-
A mouse kindling model of perimenstrual catamenial epilepsy.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Jun;341(3):784-93. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.192377. Epub 2012 Mar 20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22434675 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Anticonvulsant Properties of Aqueous Ethanolic Extracts of the Leaves, Roots, and Fruits of Jatropha gossypifolia L. (Euphorbiaceae).Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2021 Jun 11;2021:5547353. doi: 10.1155/2021/5547353. eCollection 2021. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34223167 Free PMC article.
-
A novel therapeutic approach for treatment of catamenial epilepsy.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Mar;111:127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29274741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belelli D, Bolger MB, Gee KW. Anticonvulsant profile of the progesterone metabolite 5α-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989;166:325–329. - PubMed
-
- Biagini G, Baldelli E, Longo D, Pradelli L, Zini I, Rogawski MA, Avoli M. Endogenous neurosteroids modulate epileptogenesis in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Experimental Neurol. 2006;201:519–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

