Using control genes to correct for unwanted variation in microarray data
- PMID: 22101192
- PMCID: PMC3577104
- DOI: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxr034
Using control genes to correct for unwanted variation in microarray data
Abstract
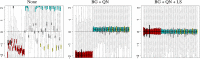
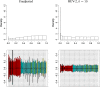
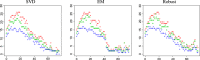
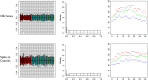
Microarray expression studies suffer from the problem of batch effects and other unwanted variation. Many methods have been proposed to adjust microarray data to mitigate the problems of unwanted variation. Several of these methods rely on factor analysis to infer the unwanted variation from the data. A central problem with this approach is the difficulty in discerning the unwanted variation from the biological variation that is of interest to the researcher. We present a new method, intended for use in differential expression studies, that attempts to overcome this problem by restricting the factor analysis to negative control genes. Negative control genes are genes known a priori not to be differentially expressed with respect to the biological factor of interest. Variation in the expression levels of these genes can therefore be assumed to be unwanted variation. We name this method "Remove Unwanted Variation, 2-step" (RUV-2). We discuss various techniques for assessing the performance of an adjustment method and compare the performance of RUV-2 with that of other commonly used adjustment methods such as Combat and Surrogate Variable Analysis (SVA). We present several example studies, each concerning genes differentially expressed with respect to gender in the brain and find that RUV-2 performs as well or better than other methods. Finally, we discuss the possibility of adapting RUV-2 for use in studies not concerned with differential expression and conclude that there may be promise but substantial challenges remain.
Figures
References
-
- Bishop CM. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. New York: Springer; 2006.
-
- Bolstad B, Collin F, Brettschneider J, Simpson K, Cope L, Irizarry R, Speed TP. Quality assessment of Affymetrix GeneChip data. In: Gentleman R, Carey V, Huber W, Irizarry R, Dudoit S, editors. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor. New York: Springer; 2005. pp. 33–47.
-
- Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:185–193. - PubMed
-
- Brettschneider J, Collin F, Bolstad BM, Speed TP. Quality assessment for short oligonucleotide microarray data. Technometrics. 2008;50:241–264.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

