Tricyclodecan-9-yl-xanthogenate (D609) mechanism of actions: a mini-review of literature
- PMID: 22101393
- PMCID: PMC3299863
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-011-0659-z
Tricyclodecan-9-yl-xanthogenate (D609) mechanism of actions: a mini-review of literature
Abstract
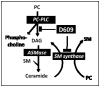
Tricyclodecan-9-yl-xanthogenate (D609) is known for its antiviral and antitumor properties. D609 actions are widely attributed to inhibiting phosphatidylcholine (PC)-specific phospholipase C (PC-PLC). D609 also inhibits sphingomyelin synthase (SMS). PC-PLC and/or SMS inhibition will affect lipid second messengers 1,2-diacylglycerol (DAG) and/or ceramide. Evidence indicates either PC-PLC and/or SMS inhibition affected the cell cycle and arrested proliferation, and stimulated differentiation in various in vitro and in vivo studies. Xanthogenate compounds are also potent antioxidants and D609 reduced Aß-induced toxicity, attributed to its antioxidant properties. Zn²⁺ is necessary for PC-PLC enzymatic activity; inhibition by D609 might be attributed to its Zn²⁺ chelation. D609 has also been proposed to inhibit acidic sphingomyelinase or down-regulate hypoxia inducible factor-1α; however these are down-stream events related to PC-PLC inhibition. Characterization of the mammalian PC-PLC is limited to inhibition of enzymatic activity (frequently measured using Amplex red assay with bacterial PC-PLC as a standard). The mammalian PC-PLC has not been cloned; sequenced and structural information is unavailable. D609 showed promise in cancer studies, reduced atherosclerotic plaques (inhibition of PC-PLC) and cerebral infarction after stroke (PC-PLC or SMS). D609 actions as an antagonist to pro-inflammatory cytokines have been attributed to PC-PLC. The purpose of this review is to comprehensively evaluate the literature and summarize the findings and relevance to cell cycle and CNS pathologies.
Figures


References
-
- Muller-Decker K. Interruption of TPA-induced signals by an antiviral and antitumoral xanthate compound: inhibition of a phospholipase C-type reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;162:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Amtmann E. The antiviral, antitumoural xanthate D609 is a competitive inhibitor of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1996;22:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Amtmann E, Mayer FK, Pink H, et al. LMV-601: Effect on HPV-16 and HPV-18 infected human cervical carcinoma cells 50th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC 2010); Boston, MA. 2010.
-
- Clark MA, Shorr RG, Bomalaski JS. Antibodies prepared to Bacillus cereus phospholipase C crossreact with a phosphatidylcholine preferring phospholipase C in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986;140:114–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

