Lyn is a redox sensor that mediates leukocyte wound attraction in vivo
- PMID: 22101434
- PMCID: PMC3228893
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10632
Lyn is a redox sensor that mediates leukocyte wound attraction in vivo
Abstract
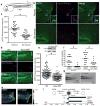
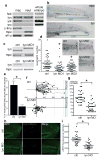
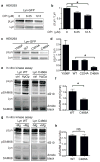
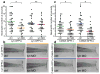
Tissue wounding induces the rapid recruitment of leukocytes. Wounds and tumours--a type of 'unhealed wound'--generate hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) through an NADPH oxidase (NOX). This extracellular H(2)O(2) mediates recruitment of leukocytes, particularly the first responders of innate immunity, neutrophils, to injured tissue. However, the sensor that neutrophils use to detect the redox state at wounds is unknown. Here we identify the Src family kinase (SFK) Lyn as a redox sensor that mediates initial neutrophil recruitment to wounds in zebrafish larvae. Lyn activation in neutrophils is dependent on wound-derived H(2)O(2) after tissue injury, and inhibition of Lyn attenuates neutrophil wound recruitment. Inhibition of SFKs also disrupted H(2)O(2)-mediated chemotaxis of primary human neutrophils. In vitro analysis identified a single cysteine residue, C466, as being responsible for direct oxidation-mediated activation of Lyn. Furthermore, transgenic-tissue-specific reconstitution with wild-type Lyn and a cysteine mutant revealed that Lyn C466 is important for the neutrophil wound response and downstream signalling in vivo. This is the first identification, to our knowledge, of a physiological redox sensor that mediates leukocyte wound attraction in multicellular organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cell migration. H2O2 sensing: the missing 'Lynk'.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Dec 7;13(1):2-3. doi: 10.1038/nrm3250. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22146747 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nathan C. Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak HF. Tumors: wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1986;315:1650–1659. - PubMed
-
- Klyubin IV, Kirpichnikova KM, Gamaley IA. Hydrogen peroxide-induced chemotaxis of mouse peritoneal neutrophils. Eur J Cell Biol. 1996;70:347–351. - PubMed
-
- Moreira S, Stramer B, Evans I, Wood W, Martin P. Prioritization of competing damage and developmental signals by migrating macrophages in the Drosophila embryo. Curr Biol. 2010;20:464–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

