A catalytically silent FAAH-1 variant drives anandamide transport in neurons
- PMID: 22101642
- PMCID: PMC3245783
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2986
A catalytically silent FAAH-1 variant drives anandamide transport in neurons
Erratum in
- Nat Neurosci. 2013 Dec;16(12):1907
Abstract
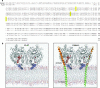
The endocannabinoid anandamide is removed from the synaptic space by a selective transport system, expressed in neurons and astrocytes, that remains molecularly uncharacterized. Here we describe a partly cytosolic variant of the intracellular anandamide-degrading enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase-1 (FAAH-1), termed FAAH-like anandamide transporter (FLAT), that lacked amidase activity but bound anandamide with low micromolar affinity and facilitated its translocation into cells. Known anandamide transport inhibitors, such as AM404 and OMDM-1, blocked these effects. We also identified a competitive antagonist of the interaction of anandamide with FLAT, the phthalazine derivative ARN272, that prevented anandamide internalization in vitro, interrupted anandamide deactivation in vivo and exerted profound analgesic effects in rodent models of nociceptive and inflammatory pain, which were mediated by CB(1) cannabinoid receptors. The results identify FLAT as a critical molecular component of anandamide transport in neural cells and a potential target for therapeutic drugs.
Figures
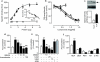
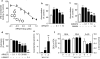

Comment in
-
Moving bliss: a new anandamide transporter.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Dec 23;15(1):5-6. doi: 10.1038/nn.3011. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22193249 No abstract available.
References
-
- Piomelli D, Astarita G, Rapaka R. A neuroscientist's guide to lipidomics. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:743–54. - PubMed
-
- Devane WA, et al. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science. 1992;258:1946–9. - PubMed
-
- Beltramo M, et al. Functional role of high-affinity anandamide transport, as revealed by selective inhibition. Science. 1997;277:1094–7. - PubMed
-
- Hillard CJ, Edgemond WS, Jarrahian A, Campbell WB. Accumulation of N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide) into cerebellar granule cells occurs via facilitated diffusion. J Neurochem. 1997;69:631–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

