Principles of dimer-specific gene regulation revealed by a comprehensive characterization of NF-κB family DNA binding
- PMID: 22101729
- PMCID: PMC3242931
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2151
Principles of dimer-specific gene regulation revealed by a comprehensive characterization of NF-κB family DNA binding
Abstract
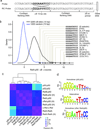
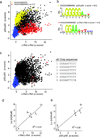
The unique DNA-binding properties of distinct NF-κB dimers influence the selective regulation of NF-κB target genes. To more thoroughly investigate these dimer-specific differences, we combined protein-binding microarrays and surface plasmon resonance to evaluate DNA sites recognized by eight different NF-κB dimers. We observed three distinct binding-specificity classes and clarified mechanisms by which dimers might regulate distinct sets of genes. We identified many new nontraditional NF-κB binding site (κB site) sequences and highlight the plasticity of NF-κB dimers in recognizing κB sites with a single consensus half-site. This study provides a database that can be used in efforts to identify NF-κB target sites and uncover gene regulatory circuitry.
Figures



References
-
- Natoli G, Saccani S, Bosisio D, Marazzi I. Interactions of NF-kappaB with chromatin: the art of being at the right place at the right time. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:439–445. - PubMed

