AHR drives the development of gut ILC22 cells and postnatal lymphoid tissues via pathways dependent on and independent of Notch
- PMID: 22101730
- PMCID: PMC3468413
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2187
AHR drives the development of gut ILC22 cells and postnatal lymphoid tissues via pathways dependent on and independent of Notch
Abstract
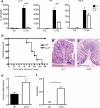
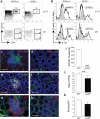
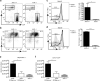
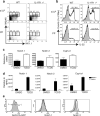
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) of the ILC22 type protect the intestinal mucosa from infection by secreting interleukin 22 (IL-22). ILC22 cells include NKp46(+) and lymphoid tissue-inducer (LTi)-like subsets that express the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). Here we found that Ahr(-/-) mice had a considerable deficit in ILC22 cells that resulted in less secretion of IL-22 and inadequate protection against intestinal bacterial infection. Ahr(-/-) mice also lacked postnatally 'imprinted' cryptopatches and isolated lymphoid follicles (ILFs), but not embryonically 'imprinted' Peyer's patches. AHR induced the transcription factor Notch, which was required for NKp46(+) ILCs, whereas LTi-like ILCs, cryptopatches and ILFs were partially dependent on Notch signaling. Thus, AHR was essential for ILC22 cells and postnatal intestinal lymphoid tissues. Moreover, ILC22 subsets were heterogeneous in their requirement for Notch and their effect on the generation of intestinal lymphoid tissues.
Figures

Comment in
-
You AhR what you eat?Nat Immunol. 2012 Jan 19;13(2):117-9. doi: 10.1038/ni.2213. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22261961 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

