Von Willebrand disease in the United States: a perspective from Wisconsin
- PMID: 22102196
- PMCID: PMC3807766
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1281039
Von Willebrand disease in the United States: a perspective from Wisconsin
Abstract
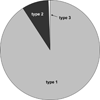
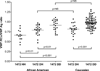
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a common bleeding disorder with prevalence in the United States of 0.01 to 1% and a prevalence in the region around Milwaukee, Wisconsin, of at least 0.025%. Care of local patients with VWD primarily occurs through our comprehensive treatment centers, although some patients are managed solely by their primary care physician or community hematologist. Type 1 VWD is the most common subtype, with more females carrying this diagnosis than males. Diagnosis and treatment in general follows guidelines outlined by the National Institutes of Health. An ongoing study, the Zimmerman Program for the Molecular and Clinical Biology of VWD, is currently enrolling patients with all VWD subtypes across the United States to better delineate the extent of VWD and correlate bleeding symptoms with laboratory findings and VWF ( Von Willebrand factor) sequence variations. Results so far have shown that VWF gene polymorphisms are common, particularly in African Americans, and may affect laboratory assays of VWF function.
© Thieme Medical Publishers.
Figures
References
-
- Werner EJ, Broxson EH, Tucker EL, Giroux DS, Shults J, Abshire TC. Prevalence of von Willebrand disease in children: a multiethnic study. J Pediatr. 1993;123(6):893–898. - PubMed
-
- Sadler JE, Mannucci PM, Berntorp E, et al. Impact, diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease. Thromb Haemost. 2000;84(2):160–174. - PubMed
-
- Weiss HJ, Ball AP, Mannucci PM. Incidence of severe von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1982;307(2):127. - PubMed
-
- Sadler JE, Budde U, Eikenboom JC, et al. Update on the pathophysiology and classification of von Willebrand disease: a report of the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(10):2103–2114. - PubMed
-
- Soucie JM, Cianfrini C, Janco RL, et al. Joint range-of-motion limitations among young males with hemophilia: prevalence and risk factors. Blood. 2004;103(7):2467–2473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

