Structure of the catalytic domain of Plasmodium falciparum ARF GTPase-activating protein (ARFGAP)
- PMID: 22102228
- PMCID: PMC3212447
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309111032507
Structure of the catalytic domain of Plasmodium falciparum ARF GTPase-activating protein (ARFGAP)
Abstract
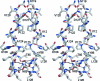
The crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the ADP ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein (ARFGAP) from Plasmodium falciparum has been determined and refined to 2.4 Å resolution. Multiwavength anomalous diffraction (MAD) data were collected utilizing the Zn(2+) ion bound at the zinc-finger domain and were used to solve the structure. The overall structure of the domain is similar to those of mammalian ARFGAPs. However, several amino-acid residues in the area where GAP interacts with ARF1 differ in P. falciparum ARFGAP. Moreover, a number of residues that form the dimer interface in the crystal structure are unique in P. falciparum ARFGAP.
© 2011 International Union of Crystallography. All rights reserved.
Figures
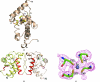



References
-
- Barton, G. J. (1993). Protein Eng. 6, 37–40. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner, F., Wiek, S., Paprotka, K., Zauner, S. & Lingelbach, K. (2001). Mol. Microbiol. 41, 1151–1158. - PubMed
-
- Bi, X., Corpina, R. A. & Goldberg, J. (2002). Nature (London), 419, 271–277. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino, J. S. & Glick, B. S. (2004). Cell, 116, 153–166. - PubMed
-
- Brünger, A. T. (1992). Nature (London), 355, 472–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

