The macromolecular complex of ICP and falcipain-2 from Plasmodium: preparation, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis
- PMID: 22102243
- PMCID: PMC3212462
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309111034592
The macromolecular complex of ICP and falcipain-2 from Plasmodium: preparation, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis
Abstract
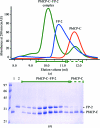
The malaria parasite Plasmodium depends on the tight control of cysteine-protease activity throughout its life cycle. Recently, the characterization of a new class of potent inhibitors of cysteine proteases (ICPs) secreted by Plasmodium has been reported. Here, the recombinant production, purification and crystallization of the inhibitory C-terminal domain of ICP from P. berghei in complex with the P. falciparum haemoglobinase falcipain-2 is described. The 1:1 complex was crystallized in space group P4(3), with unit-cell parameters a = b = 71.15, c = 120.09 Å. A complete diffraction data set was collected to a resolution of 2.6 Å.
© 2011 International Union of Crystallography. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Evans, P. (2006). Acta Cryst. D62, 72–82. - PubMed
-
- Figueiredo da Silva, A. A., de Carvalho Vieira, L., Krieger, M. A., Goldenberg, S., Zanchin, N. I. & Guimarães, B. G. (2007). J. Struct. Biol. 157, 416–423. - PubMed
-
- Hansen, G., Heitmann, A., Witt, T., Li, H., Jiang, H., Shen, X., Heussler, V. T., Rennenberg, A. & Hilgenfeld, R. (2011). Structure, 19, 919–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

