Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease: potential role in health disparities
- PMID: 22102304
- PMCID: PMC3417128
- DOI: 10.1353/hpu.2011.0161
Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease: potential role in health disparities
Abstract
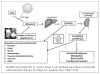
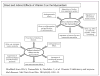
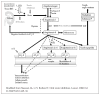
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), which includes coronary artery disease and stroke, is the leading cause of mortality in the nation. Excess CVD morbidity and premature mortality in the African American community is one of the most striking examples of racial/ ethnic disparities in health outcomes. African Americans also suffer from increased rates of hypovitaminosis D, which has emerged as an independent risk factor for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. This overview examines the potential role of hypovitaminosis D as a contributor to racial and ethnic disparities in cardiovascular disease (CVD). We review the epidemiology of vitamin D and CVD in African Americans and the emerging biological roles of vitamin D in key CVD signaling pathways that may contribute to the epidemiological findings and provide the foundation for future therapeutic strategies for reducing health disparities.
Figures



References
-
- Smedley BD, Stith AY, Nelson AR, editors. Unequal treatment: confronting racial and ethnic disparities in health care. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 2003. - PubMed
-
- Michos ED, Melamed ML. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008 Jan;11(1):7–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR033176/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MD000182/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR019234/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR003026/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022762/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD000182/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- MD000103/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003026/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR026138/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54RR022762/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007598/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR019234/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD000545/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54RR026138/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MD000545/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S21 MD000103/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
