Cleavage mediated by the P15 domain of bacterial RNase P RNA
- PMID: 22102593
- PMCID: PMC3299987
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr1001
Cleavage mediated by the P15 domain of bacterial RNase P RNA
Abstract
Independently folded domains in RNAs frequently adopt identical tertiary structures regardless of whether they are in isolation or are part of larger RNA molecules. This is exemplified by the P15 domain in the RNA subunit (RPR) of the universally conserved endoribonuclease P, which is involved in the processing of tRNA precursors. One of its domains, encompassing the P15 loop, binds to the 3'-end of tRNA precursors resulting in the formation of the RCCA-RNase P RNA interaction (interacting residues underlined) in the bacterial RPR-substrate complex. The function of this interaction was hypothesized to anchor the substrate, expose the cleavage site and result in re-coordination of Mg(2+) at the cleavage site. Here we show that small model-RNA molecules (~30 nt) carrying the P15-loop mediated cleavage at the canonical RNase P cleavage site with significantly reduced rates compared to cleavage with full-size RPR. These data provide further experimental evidence for our model that the P15 domain contributes to both substrate binding and catalysis. Our data raises intriguing evolutionary possibilities for 'RNA-mediated' cleavage of RNA.
Figures

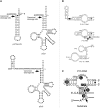
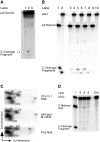
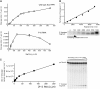

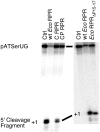
References
-
- Masquida B, Westhof E. A modular and hierarchial approach for all-atom RNA modeling. In: Gesteland RF, Cech TR, Atkins JF, editors. The RNA World. 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Press; 2006. pp. 659–681.
-
- Hendrix DK, Brenner SE, Holbrook SR. RNA structural motifs: building blocks of a molecular biomolecule. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2005;38:221–243. - PubMed
-
- Michel F, Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;216:585–610. - PubMed
-
- Murphy FL, Cech TR. An independently folding domain of RNA tertiary structure withion the Tetrahymna ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1993;32:5291–5300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

