Decrease in JAK2 V617F allele burden is not a prerequisite to clinical response in patients with polycythemia vera
- PMID: 22102708
- PMCID: PMC3347655
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.053348
Decrease in JAK2 V617F allele burden is not a prerequisite to clinical response in patients with polycythemia vera
Abstract
Background: Although reduction in the JAK2(V617F) allele burden (%V617F) has been suggested as a criterion for defining disease response to cytoreductive therapy in polycythemia vera, its value as a response monitor is unclear. The purpose of this study is to determine whether a reduction in %V617F in polycythemia vera is a prerequisite to achieving hematologic remission in response to cytoreductive therapy.
Design and methods: We compared the clinical and hematologic responses to change in %V617F (molecular response) in 73 patients with polycythemia vera treated with either interferon (rIFNα-2b: 28, Peg-rIFNα-2a: 18) or non-interferon drugs (n=27), which included hydroxyurea (n=8), imatinib (n=12), dasatinib (n=5), busulfan (n=1), and radioactive phosphorus (n=1). Hematologic response evaluation employed Polycythemia Vera Study Group criteria, and molecular response evaluation, European Leukemia Net criteria.
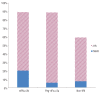
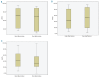
Results: Of the 46 treated with interferon, 41 (89.1%) had a hematologic response, whereas only 7 (15.2%) had a partial molecular response. Of the 27 who received non-interferon treatments, 16 (59.3%) had a hematologic response, but only 2 (7.4%) had a molecular response. Median duration of follow up was 2.8 years. Statistical agreement between hematologic response and molecular response was poor in all treatment groups.
Conclusions: Generally, hematologic response was not accompanied by molecular response. Therefore, a quantitative change in %V617F is not required for clinical response in patients with polycythemia vera.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ruxolitinib reduces JAK2 p.V617F allele burden in patients with polycythemia vera enrolled in the RESPONSE study.Ann Hematol. 2017 Jul;96(7):1113-1120. doi: 10.1007/s00277-017-2994-x. Epub 2017 Apr 30. Ann Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28456851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sustained major molecular response on interferon alpha-2b in two patients with polycythemia vera.Ann Hematol. 2008 Oct;87(10):847-50. doi: 10.1007/s00277-008-0498-4. Epub 2008 May 15. Ann Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18481066
-
[Interferon-alpha-2b induces molecular responses of patients with polycythemia vera and its post-polycythemic myelofibrosis].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;19(2):444-9. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21518505 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Where to Turn for Second-Line Cytoreduction After Hydroxyurea in Polycythemia Vera?Oncologist. 2016 Apr;21(4):475-80. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0380. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 26975864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycythemia vera: the current status of preclinical models and therapeutic targets.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Jul;24(7):615-628. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1762176. Epub 2020 May 18. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 32366208 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular responses and chromosomal aberrations in patients with polycythemia vera treated with peg-proline-interferon alpha-2b.Am J Hematol. 2015 Apr;90(4):288-94. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23928. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Am J Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25545244 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical outcomes of interferon therapy for polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Hematol. 2021 Sep;114(3):342-354. doi: 10.1007/s12185-021-03171-1. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Int J Hematol. 2021. PMID: 34091876
-
Disease modifying agents of myeloproliferative neoplasms: a review.Blood Res. 2021 Apr 30;56(S1):S26-S33. doi: 10.5045/br.2021.2020325. Blood Res. 2021. PMID: 33935032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of bone marrow morphology is essential for assessing disease status in recombinant interferon α-treated polycythemia vera patients.Haematologica. 2017 Mar;102(3):e97-e99. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.153973. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 27810993 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Optimal therapy for polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia can only be determined by the completion of randomized clinical trials.Haematologica. 2014 Jun;99(6):945-9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.106013. Haematologica. 2014. PMID: 24881037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vannucchi AM, Guglielmelli P, Tefferi A. Advances in understanding and management of myeloproliferative neoplasms. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59(3):171–91. - PubMed
-
- Wang YL, Vandris K, Jones A, Cross NC, Christos P, Adriano F, et al. JAK2 Mutations are present in all cases of polycythemia vera. Leukemia. 2008;22(6):1289. - PubMed
-
- Tefferi A, Vardiman JW. Classification and diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms: the 2008 World Health Organization criteria and point-of-care diagnostic algorithms. Leukemia. 2008;22(1):14–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

