De novo origin of human protein-coding genes
- PMID: 22102831
- PMCID: PMC3213175
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002379
De novo origin of human protein-coding genes
Abstract
The de novo origin of a new protein-coding gene from non-coding DNA is considered to be a very rare occurrence in genomes. Here we identify 60 new protein-coding genes that originated de novo on the human lineage since divergence from the chimpanzee. The functionality of these genes is supported by both transcriptional and proteomic evidence. RNA-seq data indicate that these genes have their highest expression levels in the cerebral cortex and testes, which might suggest that these genes contribute to phenotypic traits that are unique to humans, such as improved cognitive ability. Our results are inconsistent with the traditional view that the de novo origin of new genes is very rare, thus there should be greater appreciation of the importance of the de novo origination of genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
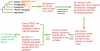
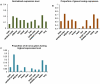
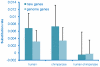
Comment in
-
De novo origins of human genes.PLoS Genet. 2011 Nov;7(11):e1002381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002381. Epub 2011 Nov 10. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22102832 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

