Folic Acid supplementation and pregnancy: more than just neural tube defect prevention
- PMID: 22102928
- PMCID: PMC3218540
Folic Acid supplementation and pregnancy: more than just neural tube defect prevention
Abstract
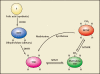
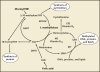
Folate (vitamin B(9)) is an essential nutrient that is required for DNA replication and as a substrate for a range of enzymatic reactions involved in amino acid synthesis and vitamin metabolism. Demands for folate increase during pregnancy because it is also required for growth and development of the fetus. Folate deficiency has been associated with abnormalities in both mothers (anemia, peripheral neuropathy) and fetuses (congenital abnormalities). This article reviews the metabolism of folic acid, the appropriate use of folic acid supplementation in pregnancy, and the potential benefits of folic acid, as well as the possible supplementation of l-methylfolate for the prevention of pregnancy-related complications other than neural tube defects.
Keywords: Dietary supplements; Folic acid; l-methylfolate.
Figures
References
-
- Prevention of neural tube defects: results of the Medical Research Council Vitamin Study. MRC Vitamin Study Research Group, authors. Lancet. 1991;338:131–137. - PubMed
-
- Rieder MJ. Prevention of neural tube defects with periconceptional folic acid. Clin Perinatol. 1994;21:483–503. - PubMed
-
- Pitkin RM. Folate and neural tube defects. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;85:285S–288S. - PubMed
-
- De Wals P, Tairou F, Van Allen MI, et al. Reduction in neural-tube defects after folic acid fortification in Canada. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:135–142. - PubMed
-
- Pietrzik K, Bailey L, Shane B. Folic acid and l-5-methyltetrahydrofolate: comparison of clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;48:535–548. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
