Separation of Betti Reaction Product Enantiomers: Absolute Configuration and Inhibition of Botulinum Neurotoxin A
- PMID: 22102940
- PMCID: PMC3217201
- DOI: 10.1021/ml200028z
Separation of Betti Reaction Product Enantiomers: Absolute Configuration and Inhibition of Botulinum Neurotoxin A
Abstract
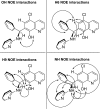
The racemic product of the Betti reaction of 5-chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline, benzaldehyde and 2-aminopyridine was separated by chiral HPLC to determine which enantiomer inhibited botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. When the enantiomers unexpectedly proved to have comparable activity, the absolute structures of (+)-(R)-1 and (-)-(S)-1 were determined by comparison of calculated and observed circular dichroism spectra. Molecular modeling studies were undertaken in an effort to understand the observed bioactivity and revealed different ensembles of binding modes, with roughly equal binding energies, for the two enantiomers.
Figures




References
-
- Roxas-Duncan V.; Enyedy I.; Montgomery V. A.; Eccard V. S.; Carrington M. A.; Lai H.; Gul N.; Yang D. C.; Smith L. A. Identification and biochemical characterization of small-molecule inhibitors of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3478–3486. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Betti M. On the addition of benzyl amine to naphthol. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1900, 30II301–309.
-
- Betti M. General condensation reaction between β-naphthol, aldehydes and amines. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1900, 30II310–316.
-
- Cardellicchio C.; Capozzi M. A. M.; Naso F. The Betti base: the awakening of a sleeping beauty. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2010, 21, 507–517.
-
- Phillips J. D. The reactions of 8-quinolinol. Chem. Rev. 1956, 56, 271–297.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

