Cerebral ketone metabolism during development and injury
- PMID: 22104087
- PMCID: PMC3306503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.09.027
Cerebral ketone metabolism during development and injury
Abstract
Cerebral metabolism of ketones is a normal part of the process of brain development. While the mature brain relies on glucose as a primary fuel source, metabolism of ketone bodies remains an alternative energy source under conditions of starvation. The neuroprotective properties of brain ketone metabolism make this alternative substrate a viable therapeutic option for various pathologies. Since the ability to revert to utilizing ketones as an alternative substrate is greatest in the younger post-weaned brain, this particular therapeutic approach remains an untapped resource particularly for pediatric pathological conditions.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
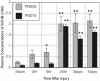
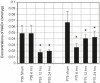
Similar articles
-
Cerebral metabolic adaptation and ketone metabolism after brain injury.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008 Jan;28(1):1-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600543. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008. PMID: 17684514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical review: ketones and brain injury.Crit Care. 2011 Apr 6;15(2):219. doi: 10.1186/cc10020. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21489321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The collective therapeutic potential of cerebral ketone metabolism in traumatic brain injury.J Lipid Res. 2014 Dec;55(12):2450-7. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R046706. Epub 2014 Apr 10. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24721741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective effects of lactate and ketone bodies in acute brain injury.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Jul;44(7):1078-1088. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241245486. Epub 2024 Apr 11. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38603600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional ketone body utilization by rat brain in starvation and diabetes.Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):E169-78. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.2.E169. Am J Physiol. 1986. PMID: 2937307
Cited by
-
Cerebral metabolism following traumatic brain injury: new discoveries with implications for treatment.Front Neurosci. 2015 Feb 9;8:408. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00408. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25709562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketogenic diet in the treatment of cancer - Where do we stand?Mol Metab. 2020 Mar;33:102-121. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.06.026. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31399389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astroglial networking contributes to neurometabolic coupling.Front Neuroenergetics. 2013 Apr 26;5:4. doi: 10.3389/fnene.2013.00004. eCollection 2013. Front Neuroenergetics. 2013. PMID: 23637659 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of SIRT3 in the Brain Under Physiological and Pathological Conditions.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Jul 25;12:196. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00196. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30090057 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in pediatric traumatic brain injury.Exp Neurol. 2019 Jul;317:168-179. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30831070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartnik BL, Sutton RL, Fukushima M, Harris NG, Hovda DA, Lee SM. Upregulation of pentose phosphate pathway and preservation of tricarboxylic acid cycle flux after experimental brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2005;22:1052–1065. - PubMed
-
- Booth RFG, Patel TB, Clark JB. The development of enzymes of energy metabolism in the brain of a precocial (guinea pig) and non-precocial (rat) species. J Neurochem. 1980;34:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Cremer JE, Braun LD, Oldendorf WH. Changes during development in transport processes of the blood-brain barrier. Biochim et Biophy Acta. 1976;448:633–637. - PubMed
-
- Dahlquist G, Persson B. The rat of cerebral utilization of glucose, ketone bodies, and oxygen: a comparative in vivo study of infant and adult rats. Pediatr Res. 1976;10:910–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

