Current status of the congenital myasthenic syndromes
- PMID: 22104196
- PMCID: PMC3269564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2011.10.009
Current status of the congenital myasthenic syndromes
Abstract
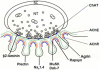
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are heterogeneous disorders in which the safety margin of neuromuscular transmission is compromised by one or more specific mechanisms. Clinical, electrophysiologic, and morphologic studies have paved the way for detecting CMS-related mutations in proteins residing in the nerve terminal, the synaptic basal lamina, and in the postsynaptic region of the motor endplate. The disease proteins identified to date include choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), the endplate species of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), β2-laminin, the acetylcholine receptor (AChR), rapsyn, plectin, Na(v)1.4, the muscle specific protein kinase (MuSK), agrin, downstream of tyrosine kinase 7 (Dok-7), and glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 1 (GFPT1). Myasthenic syndromes associated with centronuclear myopathies were recently recognized. Analysis of properties of expressed mutant proteins contributed to finding improved therapy for most CMS. Despite these advances, the molecular basis of some phenotypically characterized CMS remains elusive. Moreover, other types of CMS and disease genes likely exist and await discovery.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
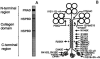

References
-
- Engel AG, Lambert EH, Gomez MR. A new myasthenic syndrome with end-plate acetylcholinesterase deficiency, small nerve terminals, and reduced acetylcholine release. Ann Neurol. 1977;1:315–330. - PubMed
-
- Beeson D, Higuchi O, Palace J, et al. Dok-7 mutations underlie a neuromuscular junction synaptopathy. Science. 2006;313:1975–1978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

