Nonlinear changes in the activity of the oxygen-dependent demethylase system in Rhodococcus erythropolis cells in the presence of low and very low doses of formaldehyde
- PMID: 22104369
- PMCID: PMC3229444
- DOI: 10.1186/1753-4631-5-9
Nonlinear changes in the activity of the oxygen-dependent demethylase system in Rhodococcus erythropolis cells in the presence of low and very low doses of formaldehyde
Abstract
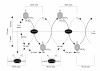
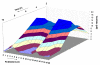
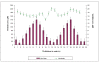
The effect of exogenous, highly diluted formaldehyde on the rate of demethylation/re-methylation of veratric acid by the bacteria Rhodococcus erythropolis was studied using electrophoretic and microscopic techniques. The activity of 4-O-demethylase, responsible for accumulation of vanillic acid, and the levels of veratric and vanillic acids were determined using capillary electrophoresis. Formaldehyde was serially diluted at 1:100 ratios, and the total number of iterations was 20. After incubation of the successive dilutions of formaldehyde with the bacteria, demethylase activity oscillated in a sinusoidal manner. It was established using capillary electrophoresis that methylation of vanillic acid to veratric acid occurred at a double rate, as shown by the doubled fluctuation in the concentration of veratrate. There were also changes in the NADH oxidase activity, which is associated with methylation processes. Microscopic observations revealed the presence of numerous enlarged vacuoles in bacterial cells during the accumulation of large amounts of vanillic acid, and their disappearance together with a decrease in 4-O-demethylase activity. The presented results give evidence for the ability of living cells to detect the presence of submolecular concentrations of biological effectors in their environment and provide a basis for a scientific explanation of the law of hormesis and the therapeutic effect of homeopathic dilutions.
Figures

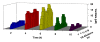





Similar articles
-
Relationships between demethylase activity, formaldehyde and oxygen during incubation of Rhodococcus erythropolis with veratrate.Acta Biol Hung. 1998;49(2-4):405-12. Acta Biol Hung. 1998. PMID: 10526986
-
Multiple respiratory bursts as a response to veratrate stress in Rhodococcus erythropolis cells.Cell Biol Int. 2000;24(8):515-27. doi: 10.1006/cbir.2000.0566. Cell Biol Int. 2000. PMID: 10924225
-
Relationship of demethylation processes to veratric acid concentration and cell density in cultures of Rhodococcus erythropolis.Cell Biol Int. 2003;27(4):325-36. doi: 10.1016/s1065-6995(02)00282-2. Cell Biol Int. 2003. PMID: 12788048
-
Microbial demethylation of lignin: Evidence of enzymes participating in the removal of methyl/methoxyl groups.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2021 Jun;147:109780. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2021.109780. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2021. PMID: 33992403 Review.
-
Biological role of formaldehyde, and cycles related to methylation, demethylation, and formaldehyde production.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003 May;3(3):175-92. doi: 10.2174/1389557033488187. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12570834 Review.
Cited by
-
Nonlinear effects of nanoparticles: biological variability from hormetic doses, small particle sizes, and dynamic adaptive interactions.Dose Response. 2013 Nov 7;12(2):202-32. doi: 10.2203/dose-response.13-025.Bell. eCollection 2014 May. Dose Response. 2013. PMID: 24910581 Free PMC article.
-
A model for homeopathic remedy effects: low dose nanoparticles, allostatic cross-adaptation, and time-dependent sensitization in a complex adaptive system.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012 Oct 22;12:191. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-191. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 23088629 Free PMC article.
-
Existence of Quantum Pharmacology in Sartans: Evidence in Isolated Rabbit Iliac Arteries.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 16;24(24):17559. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417559. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139391 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative nanomedicine: treating cancer with nanoscale natural products.Glob Adv Health Med. 2014 Jan;3(1):36-53. doi: 10.7453/gahmj.2013.009. Glob Adv Health Med. 2014. PMID: 24753994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Possible Mechanisms of Hormesis and Homeopathy in the Light of Nanopharmacology and Ultra-High Dilutions.Dose Response. 2021 Jun 14;19(2):15593258211022983. doi: 10.1177/15593258211022983. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. Dose Response. 2021. PMID: 34177397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Manninger K, Csösz M, Tyihak E. Induction of resistance of wheat plants to pathogens by pretreatment with N-methylated substances. Acta Biol Hungar. 1998;49:275–280. - PubMed
-
- Trezl L, Hullan L, Szarvas T, Csiba A, Szende B. Determination of endogenous formaldehyde in plants (fruits) bound to L-arginine and its relation to the folate cycle, photosynthesis and apoptosis. Acta Biol Hungar. 1998;49:253–264. - PubMed
-
- Weis RM, Chasalown S, Koshland DE Jr. The role of methylation in chemotaxis: an explanation of outstanding anomalies. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:6817–6826. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

