Average daily blood pressure, not office blood pressure, is associated with progression of cerebrovascular disease and cognitive decline in older people
- PMID: 22105196
- PMCID: PMC3235794
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.037036
Average daily blood pressure, not office blood pressure, is associated with progression of cerebrovascular disease and cognitive decline in older people
Abstract
Background: High blood pressure (BP) is a risk factor for cerebrovascular disease, including stroke. Little is known about the importance of BP on the progression of microvascular disease of the brain, which has been associated with functional decline in mobility and cognition in older people.
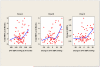
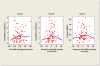
Methods and results: This was a prospective cohort of subjects 75 to 89 years of age to determine relations among vascular risk factors, white matter hyperintensity volume, and functional status. Ninety-nine subjects were enrolled through the use of a balanced 3×3 matrix stratified by age and mobility performance, and 72 subjects completed all sets of baseline and follow-up studies at 2 years. Subjects were excluded if there were medications or systemic or neurological diseases that could compromise mobility. Ambulatory and clinic BP monitoring, magnetic resonance imaging, gait studies, and neuropsychological testing were performed at baseline and after 24 months. Brain classification into normal white matter and T2-hyperintense white matter hyperintensity volume was performed with semiautomated segmentation. Quantitative measures of mobility and cognitive function were obtained longitudinally. Increased ambulatory systolic BP, but not clinic systolic BP, from baseline to 24 month follow-up was associated with increased white matter hyperintensity volume over that same period, as well as measures of executive function/processing speed. Similar associations were observed for 24-hour BP, awake BP, and sleep BP but not for the surge between the sleep and awake time at the 24-month time point.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate for the first time the importance of 24-hour systolic BP in the progression of brain white matter hyperintensity volume burden associated with impairment of cognitive function in older people. The 24-hour systolic BP may be a potential target for intervention in the elderly to reduce vascular disease of the brain and impairment of function.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter by Lagro et al regarding article, "average daily blood pressure, not office blood pressure, is associated with progression of cerebrovascular disease and cognitive decline in older people".Circulation. 2012 Jun 12;125(23):e1016; author reply e1018. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.085415. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 22689937 No abstract available.
-
Letter by castilla-guerra and fernandez-moreno regarding article, "average daily blood pressure, not office blood pressure, is associated with progression of cerebrovascular disease and cognitive decline in older people".Circulation. 2012 Jun 12;125(23):e1017; author reply e1018. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.090720. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 22689938 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vermeer SE, Den Heijer T, Koudstaal PJ, Oudkerk M, Hofman A, Breteler MM. Incidence and risk factors of silent brain infarcts in the population-based Rotterdam Scan Study. Stroke. 2003;34:392–396. - PubMed
-
- Steffens DC, Potter GG, McQuoid DR, MacFall JR, Payne ME, Burke JR, Plassman BL, Welsh-Bohmer KA. Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging vascular changes, apolipoprotein E genotype, and development of dementia in the neurocognitive outcomes of depression in the elderly study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15:839–849. - PubMed
-
- Kuller LH, Longstreth WT, Jr, Arnold AM, Bernick C, Bryan RN, Beauchamp NJ., Jr White matter hyperintensity on cranial magnetic resonance imaging: a predictor of stroke. Stroke. 2004;35:1821–1825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

