A recombinant decoy comprising EGFR and ErbB-4 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis
- PMID: 22105361
- PMCID: PMC3290749
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.518
A recombinant decoy comprising EGFR and ErbB-4 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis
Abstract
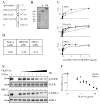
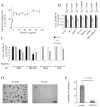
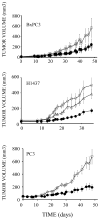
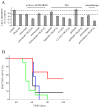
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factors control tumor progression as well as evasion from the toxic effects of chemotherapy. Accordingly, antibodies targeting the cognate receptors, such as EGFR/ErbB-1 and the co-receptor HER2/ErbB-2, are widely used to treat cancer patients, but agents that target the EGF-like growth factors are not available. To circumvent the existence of 11 distinct ErbB ligands, we constructed a soluble fusion protein (hereinafter: TRAP-Fc) comprising truncated extracellular domains of EGFR/ErbB-1 and ErbB-4. The recombinant TRAP-Fc retained high-affinity ligand binding to EGF-like growth factors and partially inhibited growth of a variety of cultured tumor cells. Consistently, TRAP-Fc displayed an inhibitory effect in xenograft models of human cancer, as well as synergy with chemotherapy. Additionally, TRAP-Fc inhibited invasive growth of mammary tumor cells and reduced their metastatic seeding in the lungs of animals. Taken together, the activities displayed by TRAP-Fc reinforce critical roles of EGF-like growth factors in tumor progression, and they warrant further tests of TRAP-Fc in preclinical models.
Figures

References
-
- Aboud-Pirak E, Hurwitz E, Pirak ME, Bellot F, Schlessinger J, Sela M. Efficacy of antibodies to epidermal growth factor receptor against KB carcinoma in vitro and in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988;80:1605–11. - PubMed
-
- Adams TE, Koziolek EJ, Hoyne PH, Bentley JD, Lu L, Lovrecz G, et al. A truncated soluble epidermal growth factor receptor-Fc fusion ligand trap displays anti-tumour activity in vivo. Growth Factors. 2009;27:141–54. - PubMed
-
- Atlas E, Cardillo M, Mehmi I, Zahedkargaran H, Tang C, Lupu R. Heregulin is sufficient for the promotion of tumorigenicity and metastasis of breast cancer cells in vivo. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:165–75. - PubMed
-
- Barozzi C, Ravaioli M, D’Errico A, Grazi GL, Poggioli G, Cavrini G, et al. Relevance of biologic markers in colorectal carcinoma: a comparative study of a broad panel. Cancer. 2002;94:647–57. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J. Targeting tyrosine kinases in cancer: the second wave. Science. 2006;312:1175–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

