Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts into dopaminergic neuron-like cells
- PMID: 22105488
- PMCID: PMC3271588
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2011.181
Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts into dopaminergic neuron-like cells
Abstract
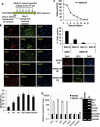
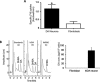
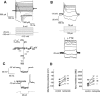
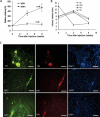
Transplantation of exogenous dopaminergic neuron (DA neurons) is a promising approach for treating Parkinson's disease (PD). However, a major stumbling block has been the lack of a reliable source of donor DA neurons. Here we show that a combination of five transcriptional factors Mash1, Ngn2, Sox2, Nurr1, and Pitx3 can directly and effectively reprogram human fibroblasts into DA neuron-like cells. The reprogrammed cells stained positive for various markers for DA neurons. They also showed characteristic DA uptake and production properties. Moreover, they exhibited DA neuron-specific electrophysiological profiles. Finally, they provided symptomatic relief in a rat PD model. Therefore, our directly reprogrammed DA neuron-like cells are a promising source of cell-replacement therapy for PD.
Figures
References
-
- Bezard E, Brotchie JM, Gross CE. Pathophysiology of levodopa-induced dyskinesia: potential for new therapies. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:577–588. - PubMed
-
- Jenner P. Molecular mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:665–677. - PubMed
-
- Brodsky MA, Nutt JG. Parkinson disease: deep brain stimulation versus best medical therapy for PD. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:530–532. - PubMed
-
- Sladek JR, Jr, Redmond DE, Jr, Collier TJ, et al. Transplantation of fetal dopamine neurons in primate brain reverses MPTP induced parkinsonism. Prog Brain Res. 1987;71:309–323. - PubMed
-
- Lindvall O, Brundin P, Widner H, et al. Grafts of fetal dopamine neurons survive and improve motor function in Parkinson's disease. Science. 1990;247:574–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DA015050/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS065353/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA136748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004216/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CA155270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA004216/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA015050/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA004216/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA131408/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS065353/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA131408/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

