Patients with biliary atresia have elevated direct/conjugated bilirubin levels shortly after birth
- PMID: 22106076
- PMCID: PMC3387898
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2011-1869
Patients with biliary atresia have elevated direct/conjugated bilirubin levels shortly after birth
Abstract
Objectives: Healthy infants are thought to acquire biliary atresia (BA) in the first weeks of life. Because those diagnosed earlier have better outcomes, we were interested in determining the earliest time BA could be detected. We started by examining the immediate postnatal period, hypothesizing that newborns would not yet have acquired disease and still have normal direct/conjugated bilirubin (DB/CB) levels.
Patients and methods: Newborn DB/CB levels were obtained retrospectively from birth hospitals. Subjects with BA were born between 2007 and 2010 and cared for at Texas Children's Hospital. Those with BA splenic malformation syndrome or born prematurely were excluded. Control subjects were term newborns who later never developed neonatal liver disease.
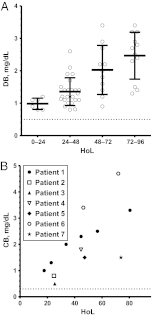
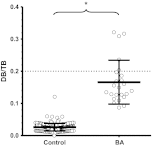
Results: Of the 61 subjects with BA, 56% had newborn DB/CB levels measured. All DB/CB levels exceeded laboratory norms and rose over time. At 24 to 48 hours of life, subjects with BA had mean DB levels significantly higher than those of controls (1.4 ± 0.43 vs. 0.19 ± 0.075 mg/dL, P < .0001), even while their mean total bilirubin (TB) levels remained below phototherapy limits. Finally, despite the elevated DB/CB levels, the majority of patients (79%) had normal DB:TB ratios ≤ 0.2.
Conclusions: Patients with BA have elevated DB/CB levels shortly after birth. To detect affected infants earlier and improve outcomes, the results suggest two possibilities: (1) screen all newborns for elevated DB/CB levels, rather than just those who appear jaundiced; and then (2) follow all newborns with elevated DB/CB levels, rather than just those with DB:TB ratios >0.2.
Figures

Comment in
-
Commentary.Clin Chem. 2015 Feb;61(2):333-4. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.229831. Clin Chem. 2015. PMID: 25632098 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Biliary atresia. Semin Immunopathol. 2009;31(3):371–381 - PubMed
-
- Hartley JL, Davenport M, Kelly DA. Biliary atresia. Lancet. 2009;374(9702):1704–1713 - PubMed
-
- Serinet MO, Wildhaber BE, Broué P, et al. Impact of age at Kasai operation on its results in late childhood and adolescence: a rational basis for biliary atresia screening. Pediatrics. 2009;123(5):1280–1286 - PubMed
-
- Davenport M, Tizzard SA, Underhill J, Mieli-Vergani G, Portmann B, Hadzic N. The biliary atresia splenic malformation syndrome: a 28-year single-center retrospective study. J Pediatr. 2006;149(3):393–400 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

