Somatostatin receptor type 2 antagonism improves glucagon and corticosterone counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 22106159
- PMCID: PMC3237655
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0690
Somatostatin receptor type 2 antagonism improves glucagon and corticosterone counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
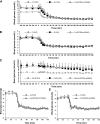
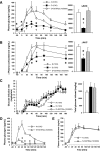
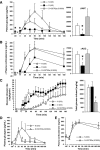
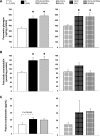
Diminished responsiveness to hypoglycemia contributes to defective counterregulation in diabetes. Pancreatic and/or circulating somatostatin are elevated in diabetes, which may inhibit counterregulatory hormone release during hypoglycemia. Thus, a selective somatostatin receptor type 2 antagonist (SSTR2a) should improve hormone counterregulation to hypoglycemia. Nondiabetic (N) and streptozotocin-induced diabetic (D) rats underwent 4-h infusion of saline or SSTR2a with insulin-induced hypoglycemia clamped at 2.5 ± 0.5 mmol/L. To evaluate the effect of the SSTR2a in the absence of hypoglycemia, rats underwent a 4-h infusion of saline (Ctrl:N, Ctrl:D) or SSTR2a (Ctrl:D+SSTR2a) only. The attenuated glucagon response to hypoglycemia in D (P < 0.0002) was fully restored by SSTR2a (P < 0.0001). Furthermore, the attenuated corticosterone response in D (P < 0.002) was also enhanced by SSTR2a (P < 0.05). In the absence of hypoglycemia, SSTR2a did not alter basal blood glucose levels. D exhibited 62% more pancreatic somatostatin than N after hypoglycemia. In N rats, SSTR2a did not augment the glucagon or corticosterone response to hypoglycemia. Thus, somatostatin may contribute to impaired glucagon responsiveness to hypoglycemia in diabetes. We demonstrate that SSTR2 antagonism enhances hypoglycemia-stimulated glucagon and corticosterone release in D but not in N rats. SSTR2 antagonism does not affect basal glycemia in D rats.
Figures
References
-
- Bolli G, de Feo P, Compagnucci P, et al. Abnormal glucose counterregulation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Interaction of anti-insulin antibodies and impaired glucagon and epinephrine secretion. Diabetes 1983;32:134–141 - PubMed
-
- Gerich JE, Langlois M, Noacco C, Karam JH, Forsham PH. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes: evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Science 1973;182:171–173 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

