Evolution of a modular software network
- PMID: 22106260
- PMCID: PMC3250116
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1115960108
Evolution of a modular software network
Abstract
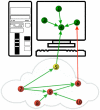
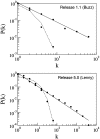
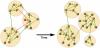
"Evolution behaves like a tinkerer" (François Jacob, Science, 1977). Software systems provide a singular opportunity to understand biological processes using concepts from network theory. The Debian GNU/Linux operating system allows us to explore the evolution of a complex network in a unique way. The modular design detected during its growth is based on the reuse of existing code in order to minimize costs during programming. The increase of modularity experienced by the system over time has not counterbalanced the increase in incompatibilities between software packages within modules. This negative effect is far from being a failure of design. A random process of package installation shows that the higher the modularity, the larger the fraction of packages working properly in a local computer. The decrease in the relative number of conflicts between packages from different modules avoids a failure in the functionality of one package spreading throughout the entire system. Some potential analogies with the evolutionary and ecological processes determining the structure of ecological networks of interacting species are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Strogatz SH. Exploring complex networks. Nature. 2001;410:268–276. - PubMed
-
- Watts DJ, Strogatz SH. Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature. 1998;393:440–442. - PubMed
-
- Barabási A-L, Albert R. Emerging of scaling in random networks. Science. 1999;286:509–512. - PubMed
-
- Jeong H, Tombor B, Albert R, Oltvai ZN, Barabási A-L. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature. 2000;407:651–654. - PubMed
-
- Liljeros F, Edling CR, Amaral LAN, Stanley HE, Aberg Y. The web of human sexual contacts. Nature. 2001;411:907–908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

