The impact of dose of the angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan on the post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 22108275
- PMCID: PMC3247852
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-247
The impact of dose of the angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan on the post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and the angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan ameliorate ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction (MI). Based on previous clinical trials, a maximum clinical dose is recommended in practical guidelines. Yet, has not been clearly demonstrated whether the recommended dose is more efficacious compared to the lower dose that is commonly used in clinical practice.
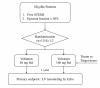
Method/design: Valsartan in post-MI remodeling (VALID) is a randomized, open-label, single-blinded multicenter study designed to compare the efficacy of different clinical dose of valsartan on the post-MI ventricular remodeling. This study also aims to assess neurohormone change and clinical parameters of patients during the post-infarct period. A total of 1116 patients with left ventricular dysfunction following the first episode of acute ST-elevation MI are to be enrolled and randomized to a maximal tolerable dose (up to 320 mg/day) or usual dose (80 mg/day) of valsartan for 12 months in 2:1 ratio. Echocardiographic analysis for quantifying post-MI ventricular remodeling is to be conducted in central core laboratory. Clinical assessment and laboratory test are performed at fixed times.
Discussion: VALID is a multicenter collaborative study to evaluate the impact of dose of valsartan on the post-MI ventricular remodeling. The results of the study provide information about optimal dosing of the drug in the management of patients after MI. The results will be available by 2012.
Trial registration: NCT01340326.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of a dose of the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan on post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodelling.ESC Heart Fail. 2018 Apr;5(2):354-363. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12249. Epub 2018 Jan 17. ESC Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29341471 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist valsartan on cardiac remodeling and left ventricular function in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction.J Med Life. 2008 Jul-Sep;1(3):323-33. J Med Life. 2008. PMID: 20108509 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of valsartan against progression of left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction: T-VENTURE study.Circ J. 2009 May;73(5):918-24. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-08-0959. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Circ J. 2009. PMID: 19346662 Clinical Trial.
-
Valsartan in the treatment of heart attack survivors.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006;2(2):125-38. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.2.125. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006. PMID: 17319456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valsartan in the treatment of heart failure or left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2007;3(4):425-30. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2007. PMID: 17969373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of a dose of the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan on post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodelling.ESC Heart Fail. 2018 Apr;5(2):354-363. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12249. Epub 2018 Jan 17. ESC Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29341471 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Aliskiren and valsartan mediate left ventricular remodeling post-myocardial infarction in mice through MMP-9 effects.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Jul;72:326-35. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.04.007. Epub 2014 Apr 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24768766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaudron P, Ellis C, Kugler I, Ertl G. Progressive left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling after myocardial infarction: potential mechanisms and early predictors. Circulation. 1993;87:755–763. - PubMed
-
- St John Sutton M, Pfeffer MA, Plapoert T. for the SAVE Investigators. Quantitative two-dimensional echocardiographic measurements are major predictor of adverse cardiovascular events after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1994;89:68–75. - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer MA, Pfeffer JM, Fishbein MC, Fletcher PJ, Spadaro J, Kloner RA, Braunwald E. Myocardial infarction size and ventricular function in rats. Circ Res. 1979;44:503–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

