Normalization as a canonical neural computation
- PMID: 22108672
- PMCID: PMC3273486
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn3136
Normalization as a canonical neural computation
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Feb;14(2):152
Abstract
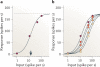
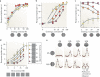
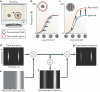
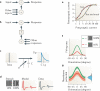
There is increasing evidence that the brain relies on a set of canonical neural computations, repeating them across brain regions and modalities to apply similar operations to different problems. A promising candidate for such a computation is normalization, in which the responses of neurons are divided by a common factor that typically includes the summed activity of a pool of neurons. Normalization was developed to explain responses in the primary visual cortex and is now thought to operate throughout the visual system, and in many other sensory modalities and brain regions. Normalization may underlie operations such as the representation of odours, the modulatory effects of visual attention, the encoding of value and the integration of multisensory information. Its presence in such a diversity of neural systems in multiple species, from invertebrates to mammals, suggests that it serves as a canonical neural computation.
Figures

References
-
- Douglas RJ, Koch C, Mahowald M, Martin KAC, Suarez HH. Recurrent excitation in neocortical circuits. Science. 1995;269:981–985. - PubMed
-
- Wang XJ. Probabilistic decision making by slow reverberation in cortical circuits. Neuron. 2002;36:955–968. - PubMed
-
- Hanes DP, Schall JD. Neural control of voluntary movement initiation. Science. 1996;274:427–430. - PubMed
-
- Lo CC, Wang XJ. Cortico-basal ganglia circuit mechanism for a decision threshold in reaction time tasks. Nature Neurosci. 2006;9:956–963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

