Structural and functional protein network analyses predict novel signaling functions for rhodopsin
- PMID: 22108793
- PMCID: PMC3261702
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2011.83
Structural and functional protein network analyses predict novel signaling functions for rhodopsin
Abstract
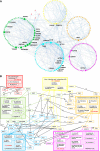
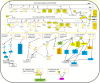
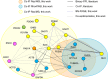
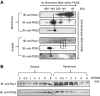
Orchestration of signaling, photoreceptor structural integrity, and maintenance needed for mammalian vision remain enigmatic. By integrating three proteomic data sets, literature mining, computational analyses, and structural information, we have generated a multiscale signal transduction network linked to the visual G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) rhodopsin, the major protein component of rod outer segments. This network was complemented by domain decomposition of protein-protein interactions and then qualified for mutually exclusive or mutually compatible interactions and ternary complex formation using structural data. The resulting information not only offers a comprehensive view of signal transduction induced by this GPCR but also suggests novel signaling routes to cytoskeleton dynamics and vesicular trafficking, predicting an important level of regulation through small GTPases. Further, it demonstrates a specific disease susceptibility of the core visual pathway due to the uniqueness of its components present mainly in the eye. As a comprehensive multiscale network, it can serve as a basis to elucidate the physiological principles of photoreceptor function, identify potential disease-associated genes and proteins, and guide the development of therapies that target specific branches of the signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Adams M, Smith UM, Logan CV, Johnson CA (2008) Recent advances in the molecular pathology, cell biology and genetics of ciliopathies. J Med Genet 45: 257–267 - PubMed
-
- Aloy P, Russell RB (2003) InterPreTS: protein interaction prediction through tertiary structure. Bioinformatics 19: 161–162 - PubMed
-
- Artemyev NO (2008) Light-dependent compartmentalization of transducin in rod photoreceptors. Mol Neurobiol 37: 44–51 - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian N, Levay K, Keren-Raifman T, Faurobert E, Slepak VZ (2001) Phosphorylation of the regulator of G protein signaling RGS9-1 by protein kinase A is a potential mechanism of light- and Ca2+-mediated regulation of G protein function in photoreceptors. Biochemistry 40: 12619–12627 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

