Dynamic multi-component covalent assembly for the reversible binding of secondary alcohols and chirality sensing
- PMID: 22109274
- PMCID: PMC3226768
- DOI: 10.1038/nchem.1198
Dynamic multi-component covalent assembly for the reversible binding of secondary alcohols and chirality sensing
Abstract
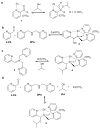
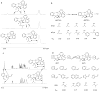
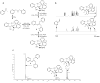
Reversible covalent bonding is often used for the creation of novel supramolecular structures, multi-component assemblies and sensing ensembles. Despite the remarkable success of dynamic covalent systems, the reversible binding of a mono-alcohol with high strength is challenging. Here, we show that a strategy of carbonyl activation and hemiaminal ether stabilization can be embodied in a four-component reversible assembly that creates a tetradentate ligand and incorporates secondary alcohols with exceptionally high affinity. Evidence is presented that the intermediate leading to binding and exchange of alcohols is an iminium ion. To demonstrate the use of this assembly process we also explored chirality sensing and enantiomeric excess determinations. An induced twist in the ligand by a chiral mono-ol results in large Cotton effects in the circular dichroism spectra indicative of the handedness of the alcohol. The strategy revealed in this study should prove broadly applicable for the incorporation of alcohols into supramolecular architecture construction.
Conflict of interest statement
Reprints and permissions information is available at
Figures

Comment in
-
Reversible covalent chemistry: Alcohols in the mix.Nat Chem. 2011 Nov 23;3(12):909-10. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1203. Nat Chem. 2011. PMID: 22109265 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Dynamic Covalent Chemistry within Biphenyl Scaffolds: Reversible Covalent Bonding, Control of Selectivity, and Chirality Sensing with a Single System.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Jan 26;57(5):1300-1305. doi: 10.1002/anie.201711602. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29239090
-
An exciton-coupled circular dichroism protocol for the determination of identity, chirality, and enantiomeric excess of chiral secondary alcohols.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Apr 25;134(16):7117-25. doi: 10.1021/ja301252h. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22439590
-
Correlating sterics parameters and diastereomeric ratio values for a multicomponent assembly to predict exciton-coupled circular dichroism intensity and thereby enantiomeric excess of chiral secondary alcohols.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Apr 25;134(16):7126-34. doi: 10.1021/ja3012534. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22439636
-
The use of circular dichroism spectroscopy for studying the chiral molecular self-assembly: an overview.Chirality. 2008 Mar;20(3-4):471-85. doi: 10.1002/chir.20459. Chirality. 2008. PMID: 17918751 Review.
-
Asymmetric autocatalysis and its application to chiral discrimination.Chirality. 2002 Jul;14(7):548-54. doi: 10.1002/chir.10081. Chirality. 2002. PMID: 12112326 Review.
Cited by
-
Optical Activity and Helicity Enhancement of Highly Sensitive Dinaphthylmethane-Based Stereodynamic Probes for Secondary Alcohols.ACS Omega. 2019 Feb 14;4(2):3244-3256. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b03337. eCollection 2019 Feb 28. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31459541 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Optical Determination of Enantiomeric Excess, Diastereomeric Excess, and Total Concentration Using Dynamic-Covalent Assemblies: A Demonstration Using 2-Aminocyclohexanol and Chemometrics.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Jul 17;141(28):11151-11160. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b03844. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31251589 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Covalent Chemistry of Aldehyde Enamines: BiIII - and ScIII -Catalysis of Amine-Enamine Exchange.Chemistry. 2017 Sep 4;23(49):11908-11912. doi: 10.1002/chem.201702363. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28722305 Free PMC article.
-
Enantioselective electrochemical detection of a L-and D-serine at polyvinylpyrrolidone-modified platinum electrode.Bioanalysis. 2024 Dec-Dec;16(23-24):1219-1227. doi: 10.1080/17576180.2024.2422209. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Bioanalysis. 2024. PMID: 39564780 Review.
-
Pyrazinyl and pyridinyl bis-azomethines formation: an experimental and computational study.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 13;13(1):17383. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44585-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37833405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rowan SJ, et al. Dynamic covalent chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2002;41:898–952. - PubMed
-
- Corbett PT, et al. Dynamic combinatorial chemistry. Chem Rev. 2006;106:3652–3711. - PubMed
-
- Lehn JM. From supramolecular chemistry towards constitutional dynamic chemistry and adaptive chemistry. Chem Soc Rev. 2007;36:151–160. - PubMed
-
- Hunt RAR, Otto S. Dynamic combinatorial libraries: new opportunities in systems chemistry. Chem Commun. 2011;47:847–858. - PubMed
-
- Mastalerz M. Shape-persistent organic cage compounds by dynamic covalent bond formation. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:5042–5053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

