Physical activity and nutrition attitudes in obese Hispanic children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 22110265
- PMCID: PMC3218153
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i39.4396
Physical activity and nutrition attitudes in obese Hispanic children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
Aim: To assess nutrition, physical activity and healthful knowledge in obese children with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH or NA) compared to children without liver disease.
Methods: Children with biopsy-proven NASH comprised the NASH group. Age, sex and ethnicity matched control groups consisted of obese (OB) and lean (CO) children with no liver disease. Subjects were administered the School Physical Activity and Nutrition Survey and one blood draw was obtained.
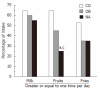
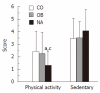
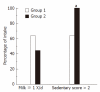
Results: Fifty-seven patients were enrolled with a mean age of 12.1 ± 2.1 years, and all were Hispanic. Even though the OB and NA had a similar increased body mass index (%), 35% of the NA group always read nutrition labels compared to none in the OB (P < 0.05), and more NA children felt their diet is "less healthy". NA consumed the least amount of fruits with only 25% having ≥ 1 fruit/d vs 45% in OB and 64.7% in CO (P < 0.05 NA vs CO). Only 15% of NA subjects performed light exercise vs 35% and 59% of OB and CO groups, respectively (P = 0.02). The mean physical activity score was lowest in the NA group (P < 0.05). Amongst the subjects with NASH, we found that 100% of patients with grade 2 or 3 fibrosis had a sedentary score > 2 compared to only 63.6% of those with grade 1 or no fibrosis (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Children with NASH had increased se-dentary behavior, decreased activity, and fruit intake. Larger studies may determine the benefit of changing these behaviors as treatment for NASH.
Keywords: Hispanic; Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; Nutrition; Nutrition survey; Pediatric; Physical activity; School physical activity.
Figures
References
-
- Xanthakos S, Miles L, Bucuvalas J, Daniels S, Garcia V, Inge T. Histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in morbidly obese adolescents. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:226–232. - PubMed
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS, Tamborlane WV, Taksali SE, Yeckel CW, Allen K, Lopes M, Savoye M, Morrison J, et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2362–2374. - PubMed
-
- Wieckowska A, Feldstein AE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the pediatric population: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2005;17:636–641. - PubMed
-
- Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the pediatric population. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:549–558, viii-ix. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

