A winged-helix transcription factor foxg1 induces expression of mss4 gene in rat hippocampal progenitor cells
- PMID: 22110345
- PMCID: PMC3214778
- DOI: 10.5607/en.2010.19.2.75
A winged-helix transcription factor foxg1 induces expression of mss4 gene in rat hippocampal progenitor cells
Abstract
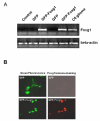
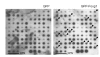
Foxg1 (previously named BF1) is a winged-helix transcription factor with restricted expression pattern in the telencephalic neuroepithelium of the neural tube and in the anterior half of the developing optic vesicle. Previous studies have shown that the targeted disruption of the Foxg1 gene leads to hypoplasia of the cerebral hemispheres with severe defect in the structures of the ventral telencephalon. To further investigate the molecular mechanisms by which Foxg1 plays essential roles during brain development, we have adopted a strategy to isolate genes whose expression changes immediately after introduction of Foxg1 in cultured neural precursor cell line, HiB5. Here, we report that seventeen genes were isolated by ordered differential displays that are up-regulated by over-expression of Foxg1, in cultured neuronal precursor cells. By nucleotide sequence comparison to known genes in the GeneBank database, we find that nine of these clones represent novel genes whose DNA sequences have not been reported. The results suggest that these genes are closely related to developmental regulation of Foxg1.
Keywords: Foxg1; Mss4; ordered-differential display; telencephalon development.
Figures

References
-
- Bourguignon C, Li J, Papalopulu N. XBF-1, a winged helix transcription factor with dual activity, has a role in positioning neurogenesis in Xenopus competent ectoderm. Development. 1998;125:4889–4900. - PubMed
-
- Danesin C, Peres JN, Johansson M, Snowden V, Cording A, Papalopulu N, Houart C. Integration of telencephalic Wnt and hedgehog signaling center activities by Foxg1. Dev Cell. 2009;16:576–587. - PubMed

