Neuroprotective Effect of Lucium chinense Fruit on Trimethyltin-Induced Learning and Memory Deficits in the Rats
- PMID: 22110372
- PMCID: PMC3214770
- DOI: 10.5607/en.2011.20.3.137
Neuroprotective Effect of Lucium chinense Fruit on Trimethyltin-Induced Learning and Memory Deficits in the Rats
Erratum in
- Exp Neurobiol. 2011 Dec;20(4):197. Bae, Hyunsu [added]
Abstract
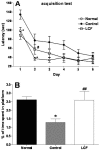
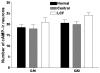
In order to the neuroprotective effect of Lycium chinense fruit (LCF), the present study examined the effects of Lycium chinense fruit on learning and memory in Morris water maze task and the choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) of rats with trimethyltin (TMT)-induced neuronal and cognitive impairments. The rats were randomly divided into the following groups: naïve rat (Normal), TMT injection+saline administered rat (control) and TMT injection+LCF administered rat (LCF). Rats were administered with saline or LCF (100 mg/kg, p.o.) daily for 2 weeks, followed by their training to the tasks. In the water maze test, the animals were trained to find a platform in a fixed position during 6d and then received 60s probe trial on the 7(th) day following removal of platform from the pool. Rats with TMT injection showed impaired learning and memory of the tasks and treatment with LCF (p<0.01) produced a significant improvement in escape latency to find the platform in the Morris water maze at the 2(nd) day. Consistent with behavioral data, treatment with LCF also slightly reduced the loss of ChAT and cAMP in the hippocampus compared to the control group. These results demonstrated that LCF has a protective effect against TMT-induced neuronal and cognitive impairments. The present study suggests that LCF might be useful in the treatment of TMT-induced learning and memory deficit.
Keywords: Lycium chinense fruit (LCF); choline acetyltransferase (ChAT); cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); trimethyltin (TMT).
Figures

References
-
- Ahi J, Radulovic J, Spiess J. The role of hippocampal signaling cascades in consolidation of fear memory. Behav Brain Res. 2004;149:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Alessandri B, FitzGerald RE, Schaeppi U, Krinke GJ, Classen W. The use of an unbaited tunnel maze in neurotoxicology: I. Trimethyltin-induced brain lesions. Neurotoxicology. 1994;15:349–357. - PubMed
-
- Andersson H, Luthman J, Lindqvist E, Olson L. Time-course of trimethyltin effects on the monoamiergic systems of the rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 1995;16:201–210. - PubMed
-
- Balaban CD, O'Callaghan JP, Billingsley ML. Trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in the rat brain: comparative studies using silver degeneration stains, immunocytochemistry and immuneassay for neuronotypic and gliotypic proteins. Neuroscience. 1988;26:337–361. - PubMed
-
- Brabeck C, Michetti F, Geloso MC, Corvino V, Goezalan F, Meyermann R, Schluesener HJ. Expression of EMAP-II by activated monocytes/microglial cells in different regions of the rat hippocampus after trimethyltin-induced brain damage. Exp Neurol. 2002;177:341–346. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

