Optimal uses of antiretrovirals for prevention in HIV-1 serodiscordant heterosexual couples in South Africa: a modelling study
- PMID: 22110407
- PMCID: PMC3217021
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001123
Optimal uses of antiretrovirals for prevention in HIV-1 serodiscordant heterosexual couples in South Africa: a modelling study
Abstract
Background: Antiretrovirals have substantial promise for HIV-1 prevention, either as antiretroviral treatment (ART) for HIV-1-infected persons to reduce infectiousness, or as pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV-1-uninfected persons to reduce the possibility of infection with HIV-1. HIV-1 serodiscordant couples in long-term partnerships (one member is infected and the other is uninfected) are a priority for prevention interventions. Earlier ART and PrEP might both reduce HIV-1 transmission in this group, but the merits and synergies of these different approaches have not been analyzed.
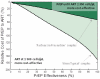
Methods and findings: We constructed a mathematical model to examine the impact and cost-effectiveness of different strategies, including earlier initiation of ART and/or PrEP, for HIV-1 prevention for serodiscordant couples. Although the cost of PrEP is high, the cost per infection averted is significantly offset by future savings in lifelong treatment, especially among couples with multiple partners, low condom use, and a high risk of transmission. In some situations, highly effective PrEP could be cost-saving overall. To keep couples alive and without a new infection, providing PrEP to the uninfected partner could be at least as cost-effective as initiating ART earlier in the infected partner, if the annual cost of PrEP is <40% of the annual cost of ART and PrEP is >70% effective.
Conclusions: Strategic use of PrEP and ART could substantially and cost-effectively reduce HIV-1 transmission in HIV-1 serodiscordant couples. New and forthcoming data on the efficacy of PrEP, the cost of delivery of ART and PrEP, and couples behaviours and preferences will be critical for optimizing the use of antiretrovirals for HIV-1 prevention. Please see later in the article for the Editors' Summary.
Conflict of interest statement
TBH has received consultancy fees from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation for work not directly related to the present work. GPG has in the past been a consultant in the field of Human Papilloma Virus research to Glaxo SmithKline and Merck, and has been a consultant in the field of stem cell transplantation to ViroPharma, but has no conflicts of interest in the HIV field. All other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. 2010. Available: http://www.unaids.org/GlobalReport/Global_report.htm. Geneva: UNAIDS.
-
- Hecht R, Stover J, Bollinger L, Muhib F, Case K, et al. Financing of HIV/AIDS programme scale-up in low-income and middle-income countries, 2009-31. Lancet. 2010;376:1254–1260. - PubMed
-
- The aids2031 Consortium. AIDS: taking a long term view. Upper Saddle River (New Jersey): FT Press; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

